A novel human immunoglobulin Fc gamma Fc epsilon bifunctional fusion protein inhibits Fc epsilon RI-mediated degranulation
- PMID: 11984598
- PMCID: PMC1866216
- DOI: 10.1038/nm0502-518
A novel human immunoglobulin Fc gamma Fc epsilon bifunctional fusion protein inhibits Fc epsilon RI-mediated degranulation
Abstract
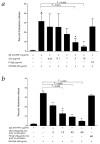
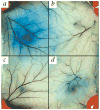
Human mast cells and basophils that express the high-affinity immunoglobulin E (IgE) receptor, Fc epsilon receptor 1 (Fc epsilon RI), have key roles in allergic diseases. Fc epsilon RI cross-linking stimulates the release of allergic mediators. Mast cells and basophils co-express Fc gamma RIIb, a low affinity receptor containing an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif and whose co-aggregation with Fc epsilon RI can block Fc epsilon RI-mediated reactivity. Here we designed, expressed and tested the human basophil and mast-cell inhibitory function of a novel chimeric fusion protein, whose structure is gamma Hinge-CH gamma 2-CH gamma 3-15aa linker-CH epsilon 2-CH epsilon 3-CH epsilon 4. This Fc gamma Fc epsilon fusion protein was expressed as the predicted 140-kappa D dimer that reacted with anti-human epsilon- and gamma-chain specific antibodies. Fc gamma Fc epsilon bound to both human Fc epsilon RI and Fc gamma RII. It also showed dose- and time-dependent inhibition of antigen-driven IgE-mediated histamine release from fresh human basophils sensitized with IgE directed against NIP (4-hydroxy-3-iodo-5-nitrophenylacetyl). This was associated with altered Syk signaling. The fusion protein also showed increased inhibition of human anti-NP (4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenylacetyl) and anti-dansyl IgE-mediated passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in transgenic mice expressing human Fc epsilon RI alpha. Our results show that this chimeric protein is able to form complexes with both Fc epsilon RI and Fc gamma RII, and inhibit mast-cell and basophil function. This approach, using a Fc gamma Fc epsilon fusion protein to co-aggregate Fc epsilon RI with a receptor containing an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif, has therapeutic potential in IgE- and Fc epsilon RI-mediated diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Ott VL, Cambier JC. Activating and inhibitory signaling in mast cells: New opportunities for therapeutic intervention? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;106:429–440. - PubMed
-
- Ravetch JV. Fc receptors. Curr Opin Immunol. 1997;9:121–125. - PubMed
-
- Daeron M, et al. The same tyrosine-based inhibition motif, in the intracytoplasmic domain of FcγRIIB, regulates negatively BCR-, TCR-, and FcR-dependent cell activation. Immunity. 1995;3:635–646. - PubMed
-
- Oliver JM, Kepley CL, Ortega E, Wilson BS. Immunogically mediated signaling in basophils and mast cells: Finding therapeutic targets for allergic diseases in the human FcεRI signaling pathway. Immunopharmacology. 2000;48:269–281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

