Modulation of K(+) currents in Xenopus spinal neurons by p2y receptors: a role for ATP and ADP in motor pattern generation
- PMID: 11986373
- PMCID: PMC2290272
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013192
Modulation of K(+) currents in Xenopus spinal neurons by p2y receptors: a role for ATP and ADP in motor pattern generation
Abstract
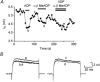
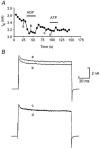
We have investigated the pharmacological properties and targets of p2y purinoceptors in Xenopus embryo spinal neurons. ATP reversibly inhibited the voltage-gated K(+) currents by 10 +/- 3 %. UTP and the analogues alpha,beta-methylene-ATP and 2-methylthio-ATP also inhibited K(+) currents. This agonist profile is similar to that reported for a p2y receptor cloned from Xenopus embryos. Voltage-gated K(+) currents could be inhibited by ADP (9 +/- 0.8 %) suggesting that a further p2y1-like receptor is also present in the embryo spinal cord. Unexpectedly we found that alpha,beta-methylene-ADP, often used to block the ecto-5'-nucleotidase, also inhibited voltage-gated K(+) currents (7 +/- 2.3 %). This inhibition was occluded by ADP, suggesting that alpha,beta-methylene-ADP is an agonist at p2y1 receptors. We have directly studied the properties of the ecto-5'-nucleotidase in Xenopus embryo spinal cord. Although ADP inhibited this enzyme, alpha,beta-methylene-ADP had no action. Caution therefore needs to be used when interpreting the actions of alpha,beta-methylene-ADP as it has previously unreported agonist activity at P2 receptors. Xenopus spinal neurons possess fast and slow voltage-gated K(+) currents. By using catechol to selectively block the fast current, we completely occluded the actions of ATP and ADP. Furthermore, the purines appeared to block only the fast relaxation component of the tail currents. We therefore conclude that the p2y receptors target only the fast component of the delayed rectifier. As ATP breakdown to ADP is rapid and ADP may accumulate at higher levels than ATP, the contribution of ADP acting through p2y1-like receptors may be an important additional mechanism for the control of spinal motor pattern generation.
Figures



References
-
- Bogdanov YD, Dale L, King BF, Whittock N, Burnstock G. Early expression of a novel nucleotide receptor in the neural plate of Xenopus embryos. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1997;272:12583–12590. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, Filippov AK, Barnard EA. Inhibition of potassium and calcium currents in neurones by molecularly-defined P2Y receptors. Journal of the Autonomic Nervous System. 2000;81:31–36. - PubMed
-
- Dale N. The isolation and identification of spinal neurons that control movement in the Xenopus embryo. European Journal of Neuroscience. 1991;3:1025–1035. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

