Diarrhea-inducing activity of avian rotavirus NSP4 glycoproteins, which differ greatly from mammalian rotavirus NSP4 glycoproteins in deduced amino acid sequence in suckling mice
- PMID: 11992013
- PMCID: PMC137017
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.11.5829-5834.2002
Diarrhea-inducing activity of avian rotavirus NSP4 glycoproteins, which differ greatly from mammalian rotavirus NSP4 glycoproteins in deduced amino acid sequence in suckling mice
Abstract
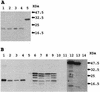
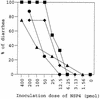
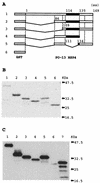
Avian rotavirus NSP4 glycoproteins expressed in Escherichia coli acted as enterotoxins in suckling mice, as did mammalian rotavirus NSP4 glycoproteins, despite great differences in the amino acid sequences. The enterotoxin domain of PO-13 NSP4 exists in amino acid residues 109 to 135, a region similar to that reported in SA11 NSP4.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sequential analysis of nonstructural protein NSP4s derived from Group A avian rotaviruses.Virus Res. 2002 Oct;89(1):145-51. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1702(02)00112-0. Virus Res. 2002. PMID: 12367757
-
Diarrhea induction by rotavirus NSP4 in the homologous mouse model system.Virology. 1999 Sep 30;262(2):398-407. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.9912. Virology. 1999. PMID: 10502518
-
Group C rotavirus NSP4 induces diarrhea in neonatal mice.Arch Virol. 2001;146(4):801-6. doi: 10.1007/s007050170148. Arch Virol. 2001. PMID: 11402865
-
How do the rotavirus NSP4 and bacterial enterotoxins lead differently to diarrhea?Virol J. 2007 Mar 21;4:31. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-4-31. Virol J. 2007. PMID: 17376232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rotavirus NSP4: a multifunctional viral enterotoxin.Viral Immunol. 2005;18(1):27-40. doi: 10.1089/vim.2005.18.27. Viral Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15802952 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Detailed computational analysis of a comprehensive set of group A rotavirus NSP4 proteins.Virus Genes. 2003 May;26(3):271-82. doi: 10.1023/a:1024451314534. Virus Genes. 2003. PMID: 12876455
-
Integrins alpha1beta1 and alpha2beta1 are receptors for the rotavirus enterotoxin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jul 1;105(26):8811-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803934105. Epub 2008 Jun 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18587047 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of human rotavirus VP6 genogroups I and II by reverse transcription-PCR.J Clin Microbiol. 2008 Oct;46(10):3330-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00432-08. Epub 2008 Jul 30. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18667595 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a G2-like porcine rotavirus bearing a novel VP4 type, P[32].Vet Res. 2010 Sep-Oct;41(5):73. doi: 10.1051/vetres/2010045. Epub 2010 Jul 29. Vet Res. 2010. PMID: 20663474 Free PMC article.
-
Rotavirus enterotoxin NSP4 binds to the extracellular matrix proteins laminin-beta3 and fibronectin.J Virol. 2004 Sep;78(18):10045-53. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.18.10045-10053.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15331737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ball, J. M., P. Tian, C. Zeng, A. P. Morris, and M. K. Estes. 1996. Age-dependent diarrhea induced by a rotaviral nonstructural glycoprotein. Science 272:101-104. - PubMed
-
- Both, G. W., A. R. Bellamy, and D. B. Mitchell. 1994. Rotavirus protein structure and function. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 185:67-105. - PubMed
-
- Bowman, G. D., I. M. Nodelman, O. Levy, S. L. Lin, P. Tian, T. J. Zamb, S. A. Udem, B. Venkataraghavan, and C. E. Schutt. 2000. Crystal structure of the oligomerization domain of NSP4 from rotavirus reveals a core metal-binding site. J. Mol. Biol. 304:861-871. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

