Hippocampal damage and exploratory preferences in rats: memory for objects, places, and contexts
- PMID: 11992015
- PMCID: PMC155935
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.41302
Hippocampal damage and exploratory preferences in rats: memory for objects, places, and contexts
Abstract
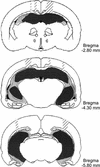
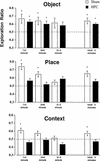
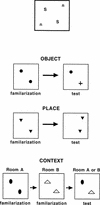
Rats have a natural tendency to spend more time exploring novel objects than familiar objects, and this preference can be used as an index of object recognition. Rats also show an exploratory preference for objects in locations where they have not previously encountered objects (an index of place memory) and for familiar objects in contexts different from those in which the objects were originally encountered (an index of context memory). In this experiment, rats with cytotoxic lesions of the hippocampal formation were tested on all three versions of the novelty-preference paradigm, with a 5-min retention interval between the familiarization and test phases. Rats with sham lesions displayed a novelty preference on all three trial types, whereas the rats with hippocampal lesions displayed a novelty preference on Object trials but did not discriminate between the objects on Place trials or Context trials. The findings indicate that hippocampal damage impairs memory for contextual or spatial aspects of an experience, whereas memory for objects that were part of the same experience are left relatively intact.
Figures
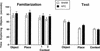
References
-
- Aggleton JP, Brown MW. Episodic memory, amnesia, and the hippocampal-anterior thalamic axis. Behav Brain Sci. 1999;22:425–444. - PubMed
-
- Aggleton JP, Hunt PR, Rawlins JNP. The effects of hippocampal lesions upon spatial and non-spatial tests of working memory. Behav Brain Res. 1986;19:133–146. - PubMed
-
- Cassaday HJ, Rawlins JNP. The hippocampus, objects, and their contexts. Behav Neurosci. 1997;111:1228–1244. - PubMed
-
- Clark RE, West AN, Zola SM, Squire LR. Rats with lesions of the hippocampus are impaired on the delayed nonmatching-to-sample task. Hippocampus. 2001;11:176–186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
