Modeling civil violence: an agent-based computational approach
- PMID: 11997450
- PMCID: PMC128592
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.092080199
Modeling civil violence: an agent-based computational approach
Abstract
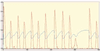
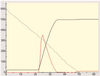
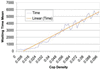
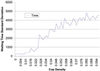
This article presents an agent-based computational model of civil violence. Two variants of the civil violence model are presented. In the first a central authority seeks to suppress decentralized rebellion. In the second a central authority seeks to suppress communal violence between two warring ethnic groups.
Figures













References
-
- Epstein J. M. & Axtell, A., (1996) Growing Artificial Societies: Social Science from the Bottom Up (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA).
-
- Collier P. (2000) J. Conflict Resolution 44, 839-850.
-
- Collier P. & Hoeffler, A. (1998) Oxford Econ. Papers 50, 563-573.
-
- Collier P. & Hoeffler, A., (1999) Justice-Seeking and Loot-Seeking in Civil War, Working Paper, April (World Bank, Washington, DC).
-
- Collier P. & Hoeffler, A., (2001) Greed and Grievance in Civil War, Policy Research Working Paper 2355 (World Bank, Washington, DC).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

