Neonatal hepatic steatosis by disruption of the adenosine kinase gene
- PMID: 11997462
- PMCID: PMC124515
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.092642899
Neonatal hepatic steatosis by disruption of the adenosine kinase gene
Abstract
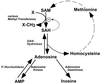
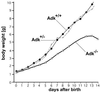
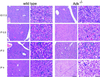
Neonatal hepatic steatosis (OMIM 228100) is a fatal condition of unknown etiology characterized by a pale and yellow liver and early postnatal mortality. In the present study, a deficit in adenosine-dependent metabolism is proposed as a causative factor. Physiologically, adenosine is efficiently metabolized to AMP by adenosine kinase (ADK), an enzyme highly expressed in liver. ADK not only ensures normal adenine nucleotide levels but also is essential for maintaining S-adenosylmethionine-dependent transmethylation processes, where adenosine, an obligatory product, has to be constantly removed. Homozygous Adk(-/-) mutants developed normally during embryogenesis. However, within 4 days after birth they displayed microvesicular hepatic steatosis and died within 14 days with fatty liver. Adenine nucleotides were decreased and S-adenosylhomocysteine, a potent inhibitor of transmethylation reactions, was increased in the mutant liver. Thus, a deficiency in adenosine metabolism is identified as a powerful contributor to the development of neonatal hepatic steatosis, providing a model for the rapid development of postnatally lethal fatty liver.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Astrogliosis in epilepsy leads to overexpression of adenosine kinase, resulting in seizure aggravation.Brain. 2005 Oct;128(Pt 10):2383-95. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh555. Epub 2005 Jun 1. Brain. 2005. PMID: 15930047
-
Mouse livers with macrosteatosis are more susceptible to normothermic ischemic injury than those with microsteatosis.J Hepatol. 2006 Apr;44(4):694-701. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.07.032. Epub 2005 Sep 2. J Hepatol. 2006. PMID: 16229921
-
Transgenic overexpression of adenosine kinase aggravates cell death in ischemia.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007 Jan;27(1):1-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600334. Epub 2006 May 10. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007. PMID: 16685255
-
Current biochemical studies of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis suggest a new therapeutic approach.Am J Gastroenterol. 2003 Sep;98(9):2093-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07670.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 14499793 Review.
-
Applying high throughput techniques in the study of adenosine kinase in plant metabolism and development.Front Biosci. 2004 May 1;9:1771-81. doi: 10.2741/1346. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 14977585 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Differences in Hepatic Metabolism between AA Broiler and Big Bone Chickens: A Proteomic Study.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 19;11(10):e0164702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164702. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27760160 Free PMC article.
-
Ketogenic diet, neuroprotection, and antiepileptogenesis.Epilepsy Res. 2020 Nov;167:106444. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2020.106444. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Epilepsy Res. 2020. PMID: 32854046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of adenosine metabolism increases risk of seizure-induced death despite decreased seizure severity.Epilepsia. 2024 Sep;65(9):2798-2811. doi: 10.1111/epi.18055. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Epilepsia. 2024. PMID: 39018000
-
Ablation of Myeloid ADK (Adenosine Kinase) Epigenetically Suppresses Atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- (Apolipoprotein E Deficient) Mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Dec;38(12):2780-2792. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311806. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 30571174 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of dysregulated adenosine homeostasis in brain disorders with a specific focus on neurodegenerative diseases.J Biomed Sci. 2021 Oct 11;28(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12929-021-00766-y. J Biomed Sci. 2021. PMID: 34635103 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Satran L, Sharp H L, Schenken J R, Krivit W. J Pediatr. 1969;75:39–46. - PubMed
-
- Burt A D, Mutton A, Day C P. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1998;15:246–258. - PubMed
-
- Fromenty B, Berson A, Pessayre D. J Hepatol. 1997;26:13–22. - PubMed
-
- Fromenty B, Pessayre D. J Hepatol. 1997;26:43–53. - PubMed
-
- Boles R G, Buck E A, Blitzer M G, Platt M S, Cowan T M, Martin S K, Yoon H, Madsen J A, Reyes-Mugica M, Rinaldo P. J Pediatr. 1998;132:924–933. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

