Interaction between the transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor/Smad pathway and beta-catenin during transforming growth factor-beta1-mediated adherens junction disassembly
- PMID: 12000714
- PMCID: PMC1850871
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)61109-1
Interaction between the transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor/Smad pathway and beta-catenin during transforming growth factor-beta1-mediated adherens junction disassembly
Abstract
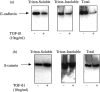
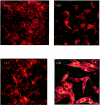
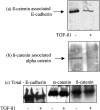
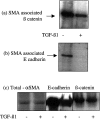
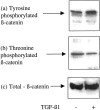
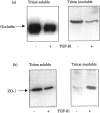
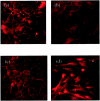
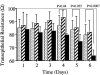
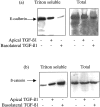
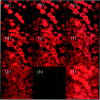
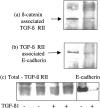
The aim of the current study was to examine the influence of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta 1 on proximal tubular epithelial cell-cell interaction, with particular emphasis on the regulation of adherens junction complex formation. Stimulation of the proximal tubular cell line HK-2 cells by TGF-beta 1 led to loss of cell-cell contact and disassembly of both adherens and tight junctional complexes. Adherens junction disassembly was associated with reduction of both Triton-soluble and Triton-insoluble E-cadherin, and an increase in detergent-soluble beta-catenin. Under these conditions, immunoprecipitation and Western analysis demonstrated decreased association of beta-catenin, both with E-cadherin, alpha-catenin, and the cell cytoskeleton. Confocal microscopy after immunostaining, showed decreased intensity of peripheral E-cadherin staining, and redistribution of beta-catenin expression to a perinuclear location. Tight junction disassembly was manifest by a reduction in the expression of Triton-soluble occludin and ZO-1 by Western analysis and their disassociation manifested by immunostaining and confocal microscopy. Loss of cell-cell contact and disassembly of adherens junctions were seen after addition of TGF-beta 1 to the basolateral aspect of the cells. Immunoprecipitation experiments demonstrated co-localization of E-cadherin, beta-catenin, and TGF-beta 1 RII in unstimulated cells. After TGF-beta 1 stimulation, the TGF-beta 1 RII no longer associated with either E-cadherin or beta-catenin. Dissociation of the adherens junction protein from the TGF-beta 1 receptor was associated with increased beta-catenin tyrosine phosphorylation and decreased threonine phosphorylation. Furthermore after receptor ligand binding, beta-catenin became associated with the TGF-beta 1-signaling molecules Smad3 and Smad4.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TGF-beta1-mediated alterations of renal proximal tubular epithelial cell phenotype.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003 Jul;285(1):F130-42. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00408.2002. Epub 2003 Mar 18. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12644442
-
Transforming growth factor-beta1 promotes invasiveness after cellular transformation with activated Ras in intestinal epithelial cells.Exp Cell Res. 2001 Jun 10;266(2):239-49. doi: 10.1006/excr.2000.5229. Exp Cell Res. 2001. PMID: 11399052
-
Polarity of response to transforming growth factor-beta1 in proximal tubular epithelial cells is regulated by beta-catenin.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 28;282(39):28639-28647. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M700594200. Epub 2007 Jul 9. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17623674
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: a key regulator in adherens junction formation and function.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jan 1;14(2):510-22. doi: 10.2741/3259. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009. PMID: 19273082 Review.
-
Advanced biosensors for nanomaterial-based detection of transforming growth factor alpha and beta, a class of major polypeptide regulators.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Feb;257(Pt 2):128622. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128622. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38065462 Review.
Cited by
-
β-Catenin/Smad3 Interaction Regulates Transforming Growth Factor-β-Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in the Lens.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 27;20(9):2078. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092078. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31035577 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin alpha3beta1-dependent beta-catenin phosphorylation links epithelial Smad signaling to cell contacts.J Cell Biol. 2009 Jan 26;184(2):309-22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200806067. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19171760 Free PMC article.
-
TGFβ modulates cell-to-cell communication in early epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Diabetologia. 2012 Mar;55(3):812-24. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2409-9. Epub 2012 Jan 4. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22215279
-
Noncanonical TGF-β signaling during mammary tumorigenesis.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2011 Jun;16(2):127-46. doi: 10.1007/s10911-011-9207-3. Epub 2011 Mar 31. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2011. PMID: 21448580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide Inhibits Transforming Growth Factor-β1-Induced EMT via Wnt/Catenin Pathway.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 13;11(1):e0147018. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147018. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26760502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bohle A, Mackensen-Haen S, Gise H: Significance of tubulointerstitial changes in the renal cortex for the excretory function and concentration ability of the kidney: a morphometric contribution. Am J Nephrol 1987, 6:421-433 - PubMed
-
- Mackensen-Haen S, Bader R, Grund KE, Bohle A: Correlations between renal cortical interstitial fibrosis, atrophy of the proximal tubules and impairment of the glomerular filtration rate. Clin Nephrol 1981, 15:167-172 - PubMed
-
- Phillips AO, Topley N, Steadman R, Morrisey K, Williams J: Induction of TGF-β1 synthesis in D-glucose primed human proximal tubular cells: differential stimulation by the macrophage derived pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNFα. Kidney Int 1996, 50:1546-1554 - PubMed
-
- Phillips AO, Topley N, Morrisey K, Williams JD, Steadman R: Basic fibroblast growth factor stimulates the release of pre-formed TGF-β1 from human proximal tubular cells in the absence of de-novo gene transcription or mRNA translation. Lab Invest 1997, 76:591-600 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

