Cytoplasmic aggregation of TRAF2 and TRAF5 proteins in the Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg cells
- PMID: 12000717
- PMCID: PMC1850879
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61112-1
Cytoplasmic aggregation of TRAF2 and TRAF5 proteins in the Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg cells
Abstract
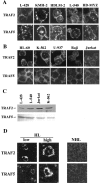
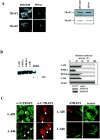
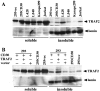
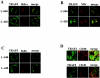
We previously reported that ligand-independent signaling by highly expressed CD30 in Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg (H-RS) cells is responsible for constitutive activation of NF-kappa B. In the present study, we characterize the intracellular localization of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor associated factor (TRAF) proteins in H-RS cells. Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy of cell lines derived from H-RS cells and HEK293 transformants highly expressing CD30 revealed aggregation of TRAF2 and TRAF5 in the cytoplasm as well as clustering near the cell membrane. In contrast, TRAF proteins were diffusely distributed in the cytoplasm in cell lines unrelated to Hodgkin's disease (HD) and control HEK293 cells. Furthermore, the same intracellular distribution of TRAF proteins was demonstrated in H-RS cells of lymph nodes of HD, but not in lymphoma cells in lymph nodes of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Dominant-negative TRAF2 and TRAF5 suppressed cytoplasmic aggregation along with constitutive NF-kappa B activation in H-RS cell lines. Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy also revealed co-localization of IKK alpha, NIK, and I kappa B alpha with aggregated TRAF proteins in H-RS cell lines. These results suggest involvement of TRAF protein aggregation in the signaling process of highly expressed CD30 and suggest they function as scaffolding proteins. Thus, cytoplasmic aggregation of TRAF proteins appears to reflect constitutive CD30 signaling which is characteristic of H-RS cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ligand-independent signaling by overexpressed CD30 drives NF-kappaB activation in Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg cells.Oncogene. 2002 Apr 11;21(16):2493-503. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205337. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 11971184
-
Expression of the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs) 1 and 2 is a characteristic feature of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells.Mod Pathol. 2000 Dec;13(12):1324-31. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3880243. Mod Pathol. 2000. PMID: 11144929
-
Transactivation of the ICAM-1 gene by CD30 in Hodgkin's lymphoma.Int J Cancer. 2006 Mar 1;118(5):1098-107. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21427. Int J Cancer. 2006. Retraction in: Int J Cancer. 2011 Dec 1;129(11):2762-3. doi: 10.1002/ijc.26387. PMID: 16152613 Retracted.
-
Hodgkin's lymphoma and CD30 signal transduction.Int J Hematol. 2003 Jan;77(1):37-47. doi: 10.1007/BF02982601. Int J Hematol. 2003. PMID: 12568298 Review.
-
The biological basis of Hodgkin's lymphoma.Drug News Perspect. 2003 Dec;16(10):649-56. doi: 10.1358/dnp.2003.16.10.829295. Drug News Perspect. 2003. PMID: 14747844 Review.
Cited by
-
Two distinct signalling cascades target the NF-kappaB regulatory factor c-IAP1 for degradation.Biochem J. 2009 Apr 28;420(1):83-91. doi: 10.1042/BJ20082140. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19243308 Free PMC article.
-
AP-1 mediated relief of repressive activity of the CD30 promoter microsatellite in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells.Am J Pathol. 2003 Aug;163(2):633-41. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63690-5. Am J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12875982 Free PMC article.
-
Brentuximab vedotin: clinical updates and practical guidance.Blood Res. 2017 Dec;52(4):243-253. doi: 10.5045/br.2017.52.4.243. Epub 2017 Dec 26. Blood Res. 2017. PMID: 29333400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular basis for the generation of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's lymphoma.Int J Hematol. 2003 May;77(4):330-5. doi: 10.1007/BF02982639. Int J Hematol. 2003. PMID: 12774919 Review.
-
Phosphorylation of TRAF2 within its RING domain inhibits stress-induced cell death by promoting IKK and suppressing JNK activation.Cancer Res. 2009 Apr 15;69(8):3665-72. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4867. Epub 2009 Mar 31. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19336568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Inoue J, Ishida T, Tsukamoto N, Kobayashi N, Naito A, Azuma S, Yamamoto T: Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) family: adapter proteins that mediate cytokine signaling. Exp Cell Res 2000, 254:14-24 - PubMed
-
- Wajant H, Henkler F, Scheurich P: The TNF-receptor-associated factor family: scaffold molecules for cytokine receptors, kinases, and their regulators. Cell Signal 2001, 13:389-400 - PubMed
-
- Malinin NL, Boldin MP, Kovalenco AV, Wallach D: MAP3K-related kinase involved in NF-κB induction by TNF. Nature 1997, 385:540-544 - PubMed
-
- Nishitoh H, Saitoh M, Mochida Y, Takeda K, Nakano H, Rothe M, Miyazono K, Ichijo H: ASK1 is essential for JNK/SAPK activation by TRAF2. Mol Cell 1998, 2:389-395 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

