Parkin localizes to the Lewy bodies of Parkinson disease and dementia with Lewy bodies
- PMID: 12000718
- PMCID: PMC1850875
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61113-3
Parkin localizes to the Lewy bodies of Parkinson disease and dementia with Lewy bodies
Abstract
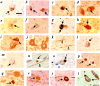
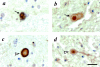
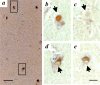
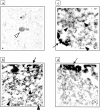
Mutations in alpha-synuclein (alpha S) and parkin cause heritable forms of Parkinson disease (PD). We hypothesized that neuronal parkin, a known E3 ubiquitin ligase, facilitates the formation of Lewy bodies (LBs), a pathological hallmark of PD. Here, we report that affinity-purified parkin antibodies labeled classical LBs in substantia nigra sections from four related human disorders: sporadic PD, inherited alphaS-linked PD, dementia with LBs (DLB), and LB-positive, parkin-linked PD. Anti-parkin antibodies also detected LBs in entorhinal and cingulate cortices from DLB brain and alphaS inclusions in sympathetic gangliocytes from sporadic PD. Double labeling with confocal microscopy of DLB midbrain sections revealed that approximately 90% of anti-alpha S-reactive LBs were also detected by a parkin antibody to amino acids 342 to 353. Accordingly, parkin proteins, including the 53-kd mature isoform, were present in affinity-isolated LBs from DLB cortex. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer and immunoelectron microscopy showed that alphaS and parkin co-localized within brainstem and cortical LBs. Biochemically, parkin appeared most enriched in cytosolic and postsynaptic fractions of adult rat brain, but also in purified, alpha S-rich presynaptic elements that additionally contained parkin's E2-binding partner, UbcH7. We conclude that parkin and UbcH7 are present with alphaS in subcellular compartments of normal brain and that parkin frequently co-localizes with alpha S aggregates in the characteristic LB inclusions of PD and DLB. These results suggest that functional parkin proteins may be required during LB formation.
Figures




References
-
- Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Diiorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL: Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 1997, 276:2045-2047 - PubMed
-
- Krüger R, Kuhn W, Muller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kosel S, Przuntek H, Epplen JT, Schols L, Riess O: Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 1998, 18:106-108 - PubMed
-
- Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, Matsumine H, Yamamura Y, Minoshima S, Yokochi M, Mizuno Y, Shimizu N: Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 1998, 392:605-608 - PubMed
-
- Lücking CB, Durr A, Bonifati V, Vaughan J, De Michele G, Gasser T, Harhangi BS, Meco G, Denefle P, Wood NW, Agid Y, Brice A: Association between early-onset Parkinson’s disease and mutations in the parkin gene. French Parkinson’s Disease Genetics Study Group. N Engl J Med 2000, 342:1560-1567 - PubMed
-
- Ujike H, Yamamoto M, Yamaguchi K, Kanzaki A, Takagi M, Kuroda S: Two cases of sporadic juvenile Parkinson’s disease caused by homozygous deletion of Parkin gene. No To Shinkei 1999, 51:1061-1064 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

