Anti-c5a ameliorates coagulation/fibrinolytic protein changes in a rat model of sepsis
- PMID: 12000738
- PMCID: PMC1850866
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61133-9
Anti-c5a ameliorates coagulation/fibrinolytic protein changes in a rat model of sepsis
Abstract
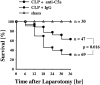
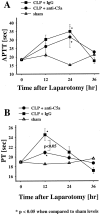
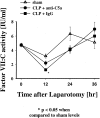
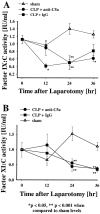
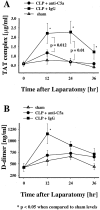
Sepsis and trauma are the two most common causes of disseminated intravascular coagulation and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Both disseminated intravascular coagulation and the systemic inflammatory response syndrome often lead to multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. The current studies have evaluated the relationship between the anaphylatoxin, C5a, and changes in the coagulation/fibrinolytic systems during the cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) model of sepsis in rats. CLP animals treated with anti-C5a had a much improved number of survivors (63%) compared to rats treated with pre-immune IgG (31%). In CLP rats treated with pre-immune IgG there was clearly increased procoagulant activity with prolongation of the activated partial thromboplastin time and prothrombin time, reduced platelet counts, and increased levels of plasma fibrinogen. Evidence for thrombin formation was indicated by early consumption of factor VII:C, subsequent consumption of factors XI:C and IX:C and anti-thrombin and increased levels of the thrombin-anti-thrombin complex and D-dimer. Limited activation of fibrinolysis was indicated by reduced plasma levels of plasminogen and increased levels of tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor. Most of these parameters were reversed in CLP rats that had been treated with anti-C5a. Production of C5a during sepsis may directly or indirectly cause hemostatic defects that can be reduced by blockade of C5a.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Theories of blood coagulation. Properties and interactions of blood clotting factors.Ann Clin Lab Sci (1971). 1971 Sep-Oct;1(2):139-54. Ann Clin Lab Sci (1971). 1971. PMID: 4949446 Review. No abstract available.
-
Theory of blood coagulation in disseminated intravascular coagulation (D. I. C.).Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch. 1972;97(1):5-19. Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch. 1972. PMID: 4114585 Review. No abstract available.
-
Coagulation pathways: interrelationships and control mechanisms.Semin Hematol. 1977 Jul;14(3):301-18. Semin Hematol. 1977. PMID: 69320 Review. No abstract available.
-
[Coagulation tests in septic surgical patients].Acta Med Croatica. 2004;58(5):389-94. Acta Med Croatica. 2004. PMID: 15756805 Croatian.
-
Basic mechanisms in blood coagulation.Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:799-829. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004055. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975. PMID: 237463 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Role of complement in multiorgan failure.Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:962927. doi: 10.1155/2012/962927. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23320021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial dysfunction and immunothrombosis in sepsis.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 4;14:1144229. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1144229. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37081895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights for C5a and C5a receptors in sepsis.Front Immunol. 2012 Dec 10;3:368. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00368. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23233853 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of plasminogen activity level in acute mesenteric ischemia.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Apr 28;14(16):2540-3. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2540. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18442202 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Naringenin in a Rat Model of Sepsis-Triggered Acute Kidney Injury via Activation of Antioxidant Enzymes and Reduction in Urinary Angiotensinogen.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Aug 11;25:5986-5991. doi: 10.12659/MSM.916400. Med Sci Monit. 2019. Retraction in: Med Sci Monit. 2025 Aug 08;31:e951047. doi: 10.12659/MSM.951047. PMID: 31401645 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Bone RC: Toward an epidemiology and natural history of SIRS (systemic inflammatory response syndrome). JAMA 1992, 268:3452-3455 - PubMed
-
- Levi M, ten Cate H, van der Poll T, van Deventer SJ: Pathogenesis of disseminated intravascular coagulation in sepsis. JAMA 1993, 270:975-979 - PubMed
-
- Gando S, Kameue T, Nanzaki S, Nakanishi Y: Cytokines, soluble thrombomodulin and disseminated intravascular coagulation in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Thromb Res 1995, 80:519-526 - PubMed
-
- Morrison DC, Kline LF: Activation of classical and properdin pathways of complement by bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS). J Immunol 1977, 118:362-368 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

