Axin-mediated CKI phosphorylation of beta-catenin at Ser 45: a molecular switch for the Wnt pathway
- PMID: 12000790
- PMCID: PMC186245
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.230302
Axin-mediated CKI phosphorylation of beta-catenin at Ser 45: a molecular switch for the Wnt pathway
Abstract
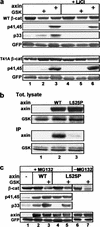
The Wnt pathway controls numerous developmental processes via the beta-catenin-TCF/LEF transcription complex. Deregulation of the pathway results in the aberrant accumulation of beta-catenin in the nucleus, often leading to cancer. Normally, cytoplasmic beta-catenin associates with APC and axin and is continuously phosphorylated by GSK-3beta, marking it for proteasomal degradation. Wnt signaling is considered to prevent GSK-3beta from phosphorylating beta-catenin, thus causing its stabilization. However, the Wnt mechanism of action has not been resolved. Here we study the regulation of beta-catenin phosphorylation and degradation by the Wnt pathway. Using mass spectrometry and phosphopeptide-specific antibodies, we show that a complex of axin and casein kinase I (CKI) induces beta-catenin phosphorylation at a single site: serine 45 (S45). Immunopurified axin and recombinant CKI phosphorylate beta-catenin in vitro at S45; CKI inhibition suppresses this phosphorylation in vivo. CKI phosphorylation creates a priming site for GSK-3beta and is both necessary and sufficient to initiate the beta-catenin phosphorylation-degradation cascade. Wnt3A signaling and Dvl overexpression suppress S45 phosphorylation, thereby precluding the initiation of the cascade. Thus, a single, CKI-dependent phosphorylation event serves as a molecular switch for the Wnt pathway.
Figures






References
-
- Ali A, Hoeflich KP, Woodgett JR. Glycogen synthase kinase-3: Properties, functions, and regulation. Chem Rev. 2001;101:2527–2540. - PubMed
-
- Bax B, Carter PS, Lewis C, Guy AR, Bridges A, Tanner R, Pettman G, Mannix C, Culbert AA, Brown MJ, et al. The structure of phosphorylated GSK-3β complexed with a peptide, FRATtide, that inhibits β-catenin phosphorylation. Structure (Camb) 2001;9:1143–1152. - PubMed
-
- Behrens J, Jerchow BA, Wurtele M, Grimm J, Asbrand C, Wirtz R, Kuhl M, Wedlich D, Birchmeier W. Functional interaction of an axin homolog, conductin, with β-catenin, APC, and GSK3β. Science. 1998;280:596–599. - PubMed
-
- Bienz M, Clevers H. Linking colorectal cancer to Wnt signaling. Cell. 2000;103:311–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
