The neglected epidemic: road traffic injuries in developing countries
- PMID: 12003888
- PMCID: PMC1123095
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.324.7346.1139
The neglected epidemic: road traffic injuries in developing countries
Figures
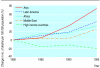
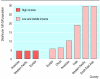
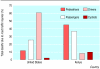
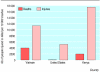
Comment in
-
War on the roads.BMJ. 2002 May 11;324(7346):1107-8. doi: 10.1136/bmj.324.7346.1107. BMJ. 2002. PMID: 12003866 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
War on the roads. People at risk get hit by traffic.BMJ. 2002 Aug 3;325(7358):277. BMJ. 2002. PMID: 12162299 No abstract available.
-
War on the roads. Evidence based prevention of these injuries is necessary.BMJ. 2002 Aug 3;325(7358):277. BMJ. 2002. PMID: 12162300 No abstract available.
References
-
- Murray C, Lopez A. The global burden of disease. Vol. 1. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1996.
-
- Krug E, editor. Injury: a leading cause of the global burden of disease. Geneva: WHO; 1999. www.who.int/violence_injury_prevention/index.html (accessed 11 Dec 2001).
-
- Jacobs G, Aaron-Thomas A, Astrop A. Estimating global road fatalities. London: Transport Research Laboratory; 2000. . (TRL Report 445).
-
- World Bank Group. Glossary. www.worldbank.org/depweb/english/modules/glossary.htm (accessed 9 March 2002).
-
- Nantulya VM, Muli-Musiime F. Kenya. Uncovering the social determinants of road traffic accidents. In: Evans T, Whitehead M, Diderichsen F, Bhuiya A, Wirth M, editors. Challenging inequities: from ethics to action. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
