Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence analyzed in a Dictyostelium discoideum host system
- PMID: 12003944
- PMCID: PMC135065
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.11.3027-3033.2002
Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence analyzed in a Dictyostelium discoideum host system
Abstract
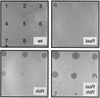
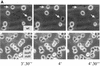
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an important opportunistic pathogen that produces a variety of cell-associated and secreted virulence factors. P. aeruginosa infections are difficult to treat effectively because of the rapid emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains. In this study, we analyzed whether the amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum can be used as a simple model system to analyze the virulence of P. aeruginosa strains. The virulent wild-type strain PAO1 was shown to inhibit growth of D. discoideum. Isogenic mutants deficient in the las quorum-sensing system were almost as inhibitory as the wild type, while rhl quorum-sensing mutants permitted growth of Dictyostelium cells. Therefore, in this model system, factors controlled by the rhl quorum-sensing system were found to play a central role. Among these, rhamnolipids secreted by the wild-type strain PAO1 could induce fast lysis of D. discoideum cells. By using this simple model system, we predicted that certain antibiotic-resistant mutants of P. aeruginosa should show reduced virulence. This result was confirmed in a rat model of acute pneumonia. Thus, D. discoideum could be used as a simple nonmammalian host system to assess pathogenicity of P. aeruginosa.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evolution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence in infected patients revealed in a Dictyostelium discoideum host model.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011 Sep;17(9):1415-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03431.x. Epub 2011 Feb 3. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011. PMID: 21091830
-
Dictyostelium transcriptional responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: common and specific effects from PAO1 and PA14 strains.BMC Microbiol. 2008 Jun 30;8:109. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-8-109. BMC Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18590548 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence using a nonmammalian host: Dictyostelium discoideum.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1149:671-80. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0473-0_51. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24818941
-
Dictyostelium as host model for pathogenesis.Cell Microbiol. 2005 Mar;7(3):307-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00493.x. Cell Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15679834 Review.
-
Impact of quorum sensing on fitness of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Int J Med Microbiol. 2006 Apr;296(2-3):93-102. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2006.01.043. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Int J Med Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16503417 Review.
Cited by
-
Genotyping of environmental and clinical Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates and their pathogenic potential.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027615. Epub 2011 Nov 15. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22110692 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated whole-genome screening for Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence genes using multiple disease models reveals that pathogenicity is host specific.Environ Microbiol. 2015 Nov;17(11):4379-93. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12863. Epub 2015 May 14. Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25845292 Free PMC article.
-
Paraburkholderia Symbionts Display Variable Infection Patterns That Are Not Predictive of Amoeba Host Outcomes.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jun 20;11(6):674. doi: 10.3390/genes11060674. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32575747 Free PMC article.
-
Rhamnolipids: diversity of structures, microbial origins and roles.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 May;86(5):1323-36. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2498-2. Epub 2010 Mar 25. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20336292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Daphnia magna, a host for evaluation of bacterial virulence.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Jan;78(2):593-5. doi: 10.1128/AEM.06278-11. Epub 2011 Nov 11. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22081563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouma, J. E., and R. E. Lenski. 1988. Evolution of a bacteria/plasmid association. Nature 335:351-352. - PubMed
-
- Burns, J. L., B. W. Ramsey, and A. L. Smith. 1993. Clinical manifestations and treatment of pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis. Adv. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 8:53-66. - PubMed
-
- Cash, H. A., D. E. Woods, B. McCullough, W. G. J. Johanson, and J. A. Bass. 1979. A rat model of chronic respiratory infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 119:453-459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

