Intraarterial suction thrombectomy in acute stroke
- PMID: 12006277
- PMCID: PMC7974726
Intraarterial suction thrombectomy in acute stroke
Abstract
Three patients with internal carotid artery thrombus and thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) 0-1 flow were treated by using intraarterial (IA) suction thrombectomy a mean of 4.2 hours after stroke onset. After catheterization with a 7F guide-catheter, thrombus was aspirated by using a 60-mL syringe. TIMI flow improved to 3 in all patients. The median National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score decreased from 22 (range, 12-23) to 4 (range, 2-22) at 3 months. IA suction thrombectomy may be safe and feasible in patients with acute stroke.
Figures
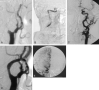


References
-
- The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 1995;333:1581–1587 - PubMed
-
- Greenberg RK, Ouriel K, Srivastava S, et al. Mechanical versus chemical thrombolysis: an in vitro differentiation of thrombolytic mechanism. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2000;11:199–205 - PubMed
-
- Mori E, Yoneda Y, Tabuchi M, et al. Intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in acute carotid artery territory stroke. Neurology 1992;42:976–982 - PubMed
-
- Lutsep HL, Campbell M, Clark WM, et al. EPAR therapy system for treatment of acute stroke: safety study results. Stroke 2001;32:319b
-
- Wikholm G. Mechanical intracranial embolectomy: a report of two cases. Intervent Neuroradiol 1998;4:159–164 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
