Apparent diffusion coefficient value of the hippocampus in patients with hippocampal sclerosis and in healthy volunteers
- PMID: 12006282
- PMCID: PMC7974737
Apparent diffusion coefficient value of the hippocampus in patients with hippocampal sclerosis and in healthy volunteers
Abstract
Background and purpose: MR diffusion-weighted (DW) imaging with apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) has had widespread use clinically in a variety of intracranial diseases; however, only a few studies report ADC changes in patients with hippocampal sclerosis. We sought to determine the ability of ADC to lateralize the epileptogenic lesion in patients with hippocampal sclerosis.
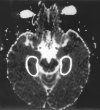
Methods: Nineteen healthy volunteers and 18 patients with intractable temporal lobe epilepsy whose MR imaging diagnosis was unilateral hippocampal sclerosis were examined prospectively with DW imaging and ADC mapping. DW images were obtained at 1.5 T with a spin-echo echo-planar sequence (6500/103 [TR/TE]) with variable diffusion gradients. ADCs were calculated from bilateral hippocampi. The ability of DW imaging and ADC to lateralize the lesion was evaluated visually and by comparing ADC values between healthy volunteers and patients with hippocampal sclerosis.
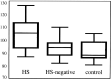
Results: In all patients, visual assessment of DW images failed to lateralize the lesion. However, the mean ADC value measured at the hippocampal area was significantly higher on the lesion side than on the contralateral side (P <.001). The overall correct lateralization rate of ADC was 100% (18 of 18 patients). Mean ADC in sclerotic hippocampi was also significantly higher than that in healthy volunteers. The normal-appearing hippocampus of the contralateral side in the patients had higher ADC values compared with those of healthy volunteers (P =.045).
Conclusion: ADC can be used as a complementary tool in lateralizing the epileptogenic lesion in patients with hippocampal sclerosis, although the practical role of ADC value is yet to be determined in patients with inconclusive MR imaging findings.
Figures
References
-
- DeCrespigny AJ, Marks MP, Enzmann DR, Moseley ME. Navigated diffusion imaging of normal and ischemic human brain. Magn Reson Med 1995;33:720–728 - PubMed
-
- Lutsep HL, Albers GW, DeCrespigny AJ, Kamat GN, Marks MP, Moseley ME. Clinical utility of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol 1997;41:574–580 - PubMed
-
- Marks MP, DeCrespigny AJ, Lentz D, Enzmann DR, Albers GW, Moseley ME. Acute and chronic stroke: navigated spin-echo diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 1996;199:403–408 - PubMed
-
- Horsfield MA, Lai M, Webb SL, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficients in benign and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis by nuclear magnetic resonance. Magn Reson Med 1996;36:393–400 - PubMed
-
- Tien RD, Felsberg GJ, Friedman H, Brown M, MacFall J. MR imaging of high-grade cerebral gliomas: value of diffusion-weighted echoplanar pulse sequences. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1994;162:671–677 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
