Targeted destruction of DNA replication protein Cdc6 by cell death pathways in mammals and yeast
- PMID: 12006651
- PMCID: PMC111125
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.02-02-0010
Targeted destruction of DNA replication protein Cdc6 by cell death pathways in mammals and yeast
Abstract
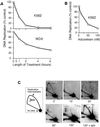
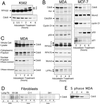
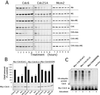
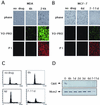
The highly conserved Cdc6 protein is required for initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication and, in yeast and Xenopus, for the coupling of DNA replication to mitosis. Herein, we show that human Cdc6 is rapidly destroyed by a p53-independent, proteasome-, and ubiquitin-dependent pathway during early stages of programmed cell death induced by the DNA-damaging drug adozelesin, or by a separate caspase-dependent pathway in cells undergoing apoptosis through an extrinsic pathway induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and cycloheximide. The proteasome-dependent pathway induced by adozelesin is conserved in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The destruction of Cdc6 may be a primordial programmed death response that uncouples DNA replication from the cell division cycle, which is reinforced in metazoans by the evolution of caspases and p53.
Figures


References
-
- Agami R, Bernards R. Distinct initiation and maintenance mechanisms cooperate to induce G1 cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage. Cell. 2000;102:55–66. - PubMed
-
- Anderson GR, Stoler DL, Brenner BM. Cancer: the evolved consequence of a destabilized genome. Bioessays. 2001;23:1037–1046. - PubMed
-
- Bhuyan BK, Smith KS, Adams EG, Petzold GL, McGovren JP. Lethality, DNA alkylation, and cell cycle effects of adozelesin (U-73975) on rodent and human cells. Cancer Res. 1992a;52:5687–5692. - PubMed
-
- Bhuyan BK, Smith KS, Adams EG, Wallace TL, Von Hoff DD, Li LH. Adozelesin, a potent new alkylating agent: cell-killing kinetics and cell-cycle effects. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1992b;30:348–354. - PubMed
-
- Brewer BJ, Fangman WL. The localization of replication origins on ARS plasmids in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1987;51:463–471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

