Peptidoglycan from Staphylococcus aureus induces tissue factor expression and procoagulant activity in human monocytes
- PMID: 12010995
- PMCID: PMC128022
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.6.3033-3039.2002
Peptidoglycan from Staphylococcus aureus induces tissue factor expression and procoagulant activity in human monocytes
Abstract
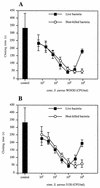
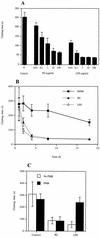
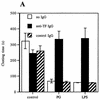
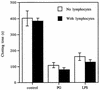
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most significant pathogens in human sepsis and endocarditis. S. aureus can initiate blood coagulation, leading to the formation of microthrombi and multiorgan dysfunction in sepsis, whereas in endocarditis the bacterium induces fibrin clots on the inner surface of the heart, so-called endocardial vegetations. In the present study, we show that live and heat-killed S. aureus bacteria are potent inducers of procoagulant activity in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Furthermore, purified peptidoglycan, the main cell wall component of S. aureus, induced procoagulant activity in mononuclear cells in a concentration-dependent fashion. The procoagulant activity in these cells was dependent on expression of tissue factor, since antibodies to tissue factor inhibited the effect of peptidoglycan. In mononuclear cells stimulated with peptidoglycan, reverse transcription-PCR showed tissue factor gene expression, and the gene product was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Finally, flow cytometry identified tissue factor at the surface of CD14-positive monocytes. Peptidoglycan is known to induce proinflammatory cytokine production in monocytes. The present investigation shows that peptidoglycan also activates the extrinsic pathway of coagulation by inducing the expression of tissue factor in these cells. This mechanism helps to explain the procoagulant activity, which plays such an important role in the pathogenicity of severe S. aureus infections.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Highly purified lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus induces procoagulant activity and tissue factor expression in human monocytes but is a weak inducer in whole blood: comparison with peptidoglycan.Infect Immun. 2004 Jul;72(7):4322-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.7.4322-4326.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15213184 Free PMC article.
-
Superantigens from Staphylococcus aureus induce procoagulant activity and monocyte tissue factor expression in whole blood and mononuclear cells via IL-1 beta.J Thromb Haemost. 2003 Dec;1(12):2569-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2003.00498.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2003. PMID: 14675093
-
Staphylococcal peptidoglycan initiates an inflammatory response and procoagulant activity in human vascular endothelial cells: a comparison with highly purified lipoteichoic acid and TSST-1.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008 Jan;52(1):110-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2007.00350.x. Epub 2007 Nov 20. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18031538
-
Role of monocytes in experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis.Infect Immun. 2000 Aug;68(8):4818-21. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.8.4818-4821.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10899897 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular regulation of tissue factor.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1990 Oct;1(4-5):415-26. doi: 10.1097/00001721-199010000-00009. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1990. PMID: 2133217 Review.
Cited by
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-induced thrombo-inflammatory response is reduced with timely antibiotic administration.Thromb Haemost. 2013 Apr;109(4):684-95. doi: 10.1160/TH12-08-0543. Epub 2013 Jan 24. Thromb Haemost. 2013. PMID: 23348831 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidoglycan induces mobilization of the surface marker for activation marker CD66b in human neutrophils but not in eosinophils.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003 May;10(3):485-8. doi: 10.1128/cdli.10.3.485-488.2003. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12738656 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus anthracis cell wall peptidoglycan but not lethal or edema toxins produces changes consistent with disseminated intravascular coagulation in a rat model.J Infect Dis. 2013 Sep;208(6):978-89. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit247. Epub 2013 Jun 3. J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23737601 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcal endocarditis presenting with a renal infarct in a patient with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cancer Res Treat. 2008 Sep;40(3):151-4. doi: 10.4143/crt.2008.40.3.151. Epub 2008 Sep 30. Cancer Res Treat. 2008. PMID: 19688123 Free PMC article.
-
Highly purified lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus induces procoagulant activity and tissue factor expression in human monocytes but is a weak inducer in whole blood: comparison with peptidoglycan.Infect Immun. 2004 Jul;72(7):4322-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.7.4322-4326.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15213184 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almdahl, S. M., J. H. Brox, and B. Österud. 1987. Mononuclear phagocyte thromboplastin and endotoxin in patients with secondary bacterial peritonitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 22:914-918. - PubMed
-
- Bick, R., and L. A. Kunkel. 1992. Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndromes. Int. J. Hematol. 55:1-26. - PubMed
-
- Cohen, J., and E. Abraham. 1999. Microbiological findings and correlation with serum tumor necrosis factor-α in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. J. Infect. Dis. 180:116-121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

