Role of interleukin-18 in host defense against disseminated Candida albicans infection
- PMID: 12011026
- PMCID: PMC127971
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.6.3284-3286.2002
Role of interleukin-18 in host defense against disseminated Candida albicans infection
Abstract
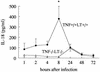
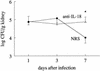
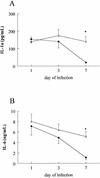
In mice injected intravenously with Candida albicans, administration of anti-interleukin-18 (IL-18) antibodies increased the yeast load in the kidneys. There was no effect on the organ load with Candida when gamma interferon (IFN-gamma)-deficient mice were treated with anti-IL-18 antibodies, suggesting that the protective effect of IL-18 is mediated through endogenous IFN-gamma.
Figures
References
-
- Balish, E., R. D. Wagner, A. Vasquez-Torres, C. Pierson, and T. Warner. 1998. Candidiasis in interferon-gamma knock-out (IFN-gamma-/-) mice. J. Infect. Dis. 178:478-487. - PubMed
-
- Joosten, L. A., F. A. van de Loo, E. Lubberts, M. M. Helsen, M. G. Netea, J. W. M. van der Meer, and W. B. van den Berg. 2000. An IFN-gamma-independent proinflammatory role of IL-18 in murine streptococcal cell wall arthritis. J. Immunol. 165:6553-6558. - PubMed
-
- Kawakami, K., Y. Koguchi, M. H. Qureshi, Y. Kinjo, S. Yara, M. Miyazato, M. Kurimoto, K. Takeda, S. Akira, and A. Saito. 2000. Reduced host resistance and Th1 response to Cryptococcus neoformans in interleukin-18 deficient mice. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 186:121-126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

