The p75 receptor transduces the signal from myelin-associated glycoprotein to Rho
- PMID: 12011108
- PMCID: PMC2173856
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200202010
The p75 receptor transduces the signal from myelin-associated glycoprotein to Rho
Abstract
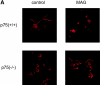
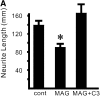
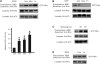
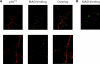
Myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) is a potent inhibitor of neurite outgrowth from a variety of neurons. The receptor for MAG or signals that elicit morphological changes in neurons remained to be established. Here we show that the neurotrophin receptor p75 (p75(NTR)) is the signal transducing element for MAG. Adult dorsal root ganglion neurons or postnatal cerebellar neurons from mice carrying a mutation in the p75(NTR) gene are insensitive to MAG with regard to neurite outgrowth. MAG activates small GTPase RhoA, leading to retarded outgrowth when p75(NTR)) is present. Colocalization of p75(NTR) and MAG binding is seen in neurons. Ganglioside GT1b, which is one of the binding partners of MAG, specifically associates with p75(NTR). Thus, p75(NTR) and GT1b may form a receptor complex for MAG to transmit the inhibitory signals in neurons.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Binding of soluble myelin-associated glycoprotein to specific gangliosides induces the association of p75NTR to lipid rafts and signal transduction.J Neurochem. 2005 Jul;94(1):15-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03121.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 15953345
-
The p75 receptor acts as a displacement factor that releases Rho from Rho-GDI.Nat Neurosci. 2003 May;6(5):461-7. doi: 10.1038/nn1045. Nat Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12692556
-
Rap1 is involved in the signal transduction of myelin-associated glycoprotein.Cell Death Differ. 2008 Feb;15(2):408-19. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402278. Epub 2007 Nov 30. Cell Death Differ. 2008. PMID: 18049479
-
p75 neurotrophin receptor signaling in the nervous system.Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2004;10:123-49. doi: 10.1016/S1387-2656(04)10005-7. Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2004. PMID: 15504705 Review.
-
Overcoming inhibitors in myelin to promote axonal regeneration.J Neurol Sci. 2005 Jun 15;233(1-2):43-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2005.03.023. Epub 2005 Apr 20. J Neurol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15949495 Review.
Cited by
-
ProNGF promotes neurite growth from a subset of NGF-dependent neurons by a p75NTR-dependent mechanism.Development. 2013 May;140(10):2108-17. doi: 10.1242/dev.085266. Development. 2013. PMID: 23633509 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiology and cellular pathogenesis of glycolipid storage diseases.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2003 May 29;358(1433):893-904. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2003.1276. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2003. PMID: 12803923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actions of neurotrophic factors and their signaling pathways in neuronal survival and axonal regeneration.Mol Neurobiol. 2006 Apr;33(2):155-79. doi: 10.1385/MN:33:2:155. Mol Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16603794 Review.
-
Nogo-A and myelin-associated glycoprotein mediate neurite growth inhibition by antagonistic regulation of RhoA and Rac1.J Neurosci. 2002 Dec 1;22(23):10368-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-23-10368.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12451136 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic or Non-synaptic? Different Intercellular Interactions with Retinal Ganglion Cells in Optic Nerve Regeneration.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 May;59(5):3052-3072. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02781-y. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35266115 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Borasio, G.D., J. John, A. Wittinghofer, Y.A. Barde, M. Sendtner, and R. Heumann. 1989. ras p21 protein promotes survival and fiber outgrowth of cultured embryonic neurons. Neuron. 2:1087–1096. - PubMed
-
- Cai, D., Y. Shen, M. De Bellard, S. Tang, and M.T. Filbin. 1999. Prior exposure to neurotrophins blocks inhibition of axonal regeneration by MAG and myelin via a cAMP-dependent mechanism. Neuron. 22:89–101. - PubMed
-
- Davies, A.M. 2000. Neurotrophins: neurotrophic modulation of neurite growth. Curr. Biol. 10:R198–R200. - PubMed
-
- Ernfors, P., F. Hallbook, T. Ebendal, E.M. Shooter, M.J. Radeke, T.P. Misko, and H. Persson. 1988. Developmental and regional expression of beta-nerve growth factor receptor mRNA in the chick and rat. Neuron. 1:983–996. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

