Preferential binding of ATR protein to UV-damaged DNA
- PMID: 12011431
- PMCID: PMC124461
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.102167799
Preferential binding of ATR protein to UV-damaged DNA
Abstract
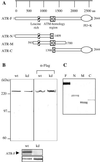
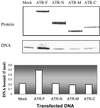
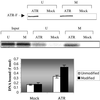
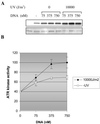
The ATR protein is a member of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-related kinase family and plays an important role in UV-induced DNA damage checkpoint response. Its role as a signal transducer in cell cycle checkpoint is well established, but it is currently unclear whether ATR functions as a damage sensor as well. Here we have purified the ATR protein and investigated its interaction with DNA by using biochemical analysis and electron microscopy. We find that ATR is a DNA-binding protein with higher affinity to UV-damaged than undamaged DNA. In addition, damaged DNA stimulates the kinase activity of ATR to a significantly higher level than undamaged DNA. Our data suggest that ATR may function as an initial sensor in the DNA damage checkpoint response.
Figures


References
-
- Abraham R T. Genes Dev. 2001;15:2177–2196. - PubMed
-
- Lowndes N F, Murguia J R. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2000;10:17–25. - PubMed
-
- Zhou B B, Elledge S J. Nature (London) 2000;408:433–439. - PubMed
-
- Shiloh Y. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2001;11:71–77. - PubMed
-
- Durocher D, Jackson S P. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13:225–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

