A small-systems approach to motor pattern generation
- PMID: 12015615
- PMCID: PMC6494453
- DOI: 10.1038/417343a
A small-systems approach to motor pattern generation
Abstract
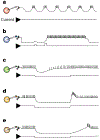
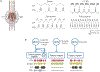
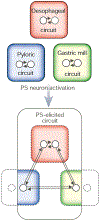
How neuronal networks enable animals, humans included, to make coordinated movements is a continuing goal of neuroscience research. The stomatogastric nervous system of decapod crustaceans, which contains a set of distinct but interacting motor circuits, has contributed significantly to the general principles guiding our present understanding of how rhythmic motor circuits operate at the cellular level. This results from a detailed documentation of the circuit dynamics underlying motor pattern generation in this system as well as its modulation by individual transmitters and neurons.
Figures
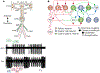
References
-
- Marder E & Calabrese RL Principles of rhythmic motor pattern generation. Physiol. Rev 76, 687–717 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Stein PSG, Grillner S, Selverston AI & Stuart DG (eds) Neurons, Networks, and Motor Behavior (The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1997).
-
- Marder E & Bucher D Central pattern generators and the control of rhythmic movements. Curr. Biol 11, R986–R996 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Pearson KG Neural adaptation in the generation of rhythmic behavior. Annu. Rev. Physiol 62, 723–753 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

