Role of phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate organization in membrane transport by the Unc104 kinesin motor
- PMID: 12015984
- PMCID: PMC2851634
- DOI: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00708-0
Role of phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate organization in membrane transport by the Unc104 kinesin motor
Abstract
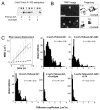
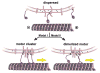
Unc104 (KIF1A) kinesin transports membrane vesicles along microtubules in lower and higher eukaryotes. Using an in vitro motility assay, we show that Unc104 uses a lipid binding pleckstrin homology (PH) domain to dock onto membrane cargo. Through its PH domain, Unc104 can transport phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2)-containing liposomes with similar properties to native vesicles. Interestingly, liposome movement by monomeric Unc104 motors shows a very steep dependence on PtdIns(4,5)P2 concentration (Hill coefficient of approximately 20), even though liposome binding is noncooperative. This switch-like transition for movement can be shifted to lower PtdIns(4,5)P2 concentrations by the addition of cholesterol/sphingomyelin or GM1 ganglioside/cholera toxin, conditions that produce raft-like behavior of Unc104 bound to lipid bilayers. These studies suggest that clustering of Unc104 in PtdIns(4,5)P2-containing rafts provides a trigger for membrane transport.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The lipid binding pleckstrin homology domain in UNC-104 kinesin is necessary for synaptic vesicle transport in Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Aug;15(8):3729-39. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-04-0326. Epub 2004 May 21. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15155810 Free PMC article.
-
Conversion of Unc104/KIF1A kinesin into a processive motor after dimerization.Science. 2002 Sep 27;297(5590):2263-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1073386. Science. 2002. PMID: 12351789
-
Analysis of the weak interactions of ADP-Unc104 and ADP-kinesin with microtubules and their inhibition by MAP2c.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2007 May;64(5):377-89. doi: 10.1002/cm.20190. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2007. PMID: 17326138
-
Rafting along the axon on Unc104 motors.Dev Cell. 2002 May;2(5):515-6. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(02)00177-6. Dev Cell. 2002. PMID: 12015956 Review.
-
Spatial control of actin-based motility through plasmalemmal PtdIns(4,5)P2-rich raft assemblies.Biochem Soc Symp. 2005;(72):119-27. doi: 10.1042/bss0720119. Biochem Soc Symp. 2005. PMID: 15649136 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Characterization of Mutations Related to Conidiophore Stalk Length Development in Aspergillus niger Laboratory Strain N402.Front Genet. 2021 Apr 20;12:666684. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.666684. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33959152 Free PMC article.
-
The balance between capture and dissociation of presynaptic proteins controls the spatial distribution of synapses.Neuron. 2013 Jun 19;78(6):994-1011. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.04.035. Epub 2013 May 30. Neuron. 2013. PMID: 23727120 Free PMC article.
-
Apical trafficking in epithelial cells: signals, clusters and motors.J Cell Sci. 2009 Dec 1;122(Pt 23):4253-66. doi: 10.1242/jcs.032615. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19923269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The architecture of kinesin-3 KLP-6 reveals a multilevel-lockdown mechanism for autoinhibition.Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 25;13(1):4281. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32048-y. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35879313 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of lysosomal positioning and movement.Traffic. 2018 Oct;19(10):761-769. doi: 10.1111/tra.12587. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Traffic. 2018. PMID: 29900632 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berg JS, Derfler BH, Pennisi CM, Corey DP, Cheney RE. Myosin-X, a novel myosin with pleckstrin homology domains, associates with regions of dynamic actin. J Cell Sci. 2000;113:3439–3451. - PubMed
-
- Bloom GS. The UNC-104/KIF1 family of kinesins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13:36–40. - PubMed
-
- Case RB, Pierce DW, Hom-Booher N, Hart CL, Vale RD. The directional preference of kinesin motors is specified by an element outside of the motor catalytic domain. Cell. 1997;90:959–966. - PubMed
-
- Cohn RC, Poncz L, Waller RL, Dearborn DG. Phosphoinositide content of erythrocyte membranes in cystic fibrosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1988;111:336–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

