Antibacterial activities and characterization of novel inhibitors of LpxC
- PMID: 12019092
- PMCID: PMC127247
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.6.1793-1799.2002
Antibacterial activities and characterization of novel inhibitors of LpxC
Abstract
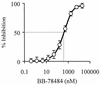
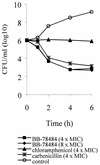
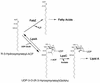
Lipid A is the hydrophobic anchor of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and forms the major lipid component of the outer monolayer of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. Lipid A is required for bacterial growth and virulence, and inhibition of its biosynthesis is lethal to bacteria. UDP-3-O-(R-3-hydroxymyristoyl)-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase (LpxC) is a metalloenzyme that catalyzes the second step in the biosynthesis of lipid A. Inhibitors of LpxC have previously been shown to have antibiotic activities. We have screened a metalloenzyme inhibitor library for antibacterial activities against an Escherichia coli strain with reduced LpxC activity. From this screen, a series of sulfonamide derivatives of the alpha-(R)-amino hydroxamic acids, exemplified by BB-78484 and BB-78485, have been identified as having potent inhibitory activities against LpxC in an in vitro assay. Leads from this series showed gram-negative selective activities against members of the Enterobacteriaceae, Serratia marcescens, Morganella morganii, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Burkholderia cepacia. BB-78484 was bactericidal against E. coli, achieving 3-log killing in 4 h at a concentration 4 times above the MIC, as would be predicted for an inhibitor of lipid A biosynthesis. E. coli mutants with decreased susceptibility to BB-78484 were selected. Analysis of these mutants revealed that resistance arose as a consequence of mutations in the fabZ or lpxC genes. These data confirm the antibacterial target of BB-78484 and BB-78485 and validate LpxC as a target for gram-negative selective antibacterials.
Figures
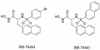

References
-
- Anderson, M. S., H. G. Bull, S. M. Galloway, T. M. Kelly, S. Mohan, K. Radika, and C. R. H. Raetz. 1993. UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase of Escherichia coli. The first step of endotoxin biosynthesis is thermodynamically unfavorable. J. Biol. Chem. 268:19858-19865. - PubMed
-
- Beckett, R. P., A. H. Davidson, A. H. Drummond, P. Huxley, and M. Whittaker. 1996. Recent advances in matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor research. Drug Discov. Today 1:16-26. - PubMed
-
- Chen, M. H., M. G. Steiner, S. E. de Laszlo, A. A. Patchett, M. S. Anderson, S. A. Hyland, H. R. Onishi, L. L. Silver, and C. R. H. Raetz. 1999. Carbohydroxamido-oxazolidines: antibacterial agents that target lipid A biosynthesis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 9:313-318. - PubMed
-
- Clements, J. M., R. P. Beckett, A. Brown, G. Catlin, M. Lobell, S. Palan, W. Thomas, M. Whittaker, S. Wood, S. Salama, P. J. Baker, H. F. Rodgers, V Barynin, D. W. Rice, and M. G. Hunter. 2001. Antibiotic activity and characterization of BB-3497, a novel peptide deformylase inhibitor. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 45:563-570. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

