Efficacy of antifungal therapy in a nonneutropenic murine model of zygomycosis
- PMID: 12019114
- PMCID: PMC127262
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.6.1953-1959.2002
Efficacy of antifungal therapy in a nonneutropenic murine model of zygomycosis
Abstract
Three isolates of zygomycetes belonging to three different genera (Rhizopus microsporus, Absidia corymbifera, and Apophysomyces elegans) were used to produce a disseminated infection in nonimmunocompromised mice. The therapeutic efficacy of amphotericin B, given intraperitoneally at doses ranging from 0.5 to 4.5 mg/kg of body weight/day, oral itraconazole at 100 mg/kg/day, and oral terbinafine at 150 mg/kg/day was evaluated in this model. The markers of antifungal efficacy were the median survival time, the mortality rate, and the percentage of infected organs. Organ culture was performed along with microscopic direct examinations of tissues to assess the presence of an active infection. An acute and lethal infection was obtained in untreated mice challenged with each of the three strains. The data obtained for direct examinations and qualitative cultures indicate that, due to the nonseptate nature of the hyphae, each technique gives different information and should be used together with the others. Against all three strains, amphotericin B yielded a 90 to 100% survival rate. Itraconazole was inactive against R. microsporus but significantly reduced mortality in mice infected with A. corymbifera or A. elegans. Terbinafine had no beneficial effects against R. microsporus and A. corymbifera despite documented absorption of the drug. Overall, only limited correlations were observed between MICs determined in vitro and in vivo efficacy of the drugs. The efficacy of itraconazole in these models of zygomycosis suggests that this drug, as well as the new azole compounds presently under development, warrants close evaluation.
Figures
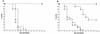
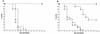
Similar articles
-
Activity of posaconazole in treatment of experimental disseminated zygomycosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 Nov;47(11):3647-50. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.11.3647-3650.2003. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. PMID: 14576138 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo activities of posaconazole against zygomycetes with various degrees of susceptibility.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010 Oct;65(10):2158-63. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkq276. Epub 2010 Jul 28. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20667887
-
Posaconazole prophylaxis in experimental systemic zygomycosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Jan;51(1):73-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00969-06. Epub 2006 Oct 23. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17060525 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models of zygomycosis--Absidia, Rhizopus, Rhizomucor, and Cunninghamella.Mycopathologia. 2001;152(1):5-13. doi: 10.1023/a:1011900630987. Mycopathologia. 2001. PMID: 11694096 Review.
-
Zygomycosis--a case report and overview of the disease in India.Mycoses. 2007 Jul;50(4):247-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2007.01382.x. Mycoses. 2007. PMID: 17576314 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis and treatment of mucormycosis in patients with hematological malignancies: guidelines from the 3rd European Conference on Infections in Leukemia (ECIL 3).Haematologica. 2013 Apr;98(4):492-504. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2012.065110. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Haematologica. 2013. PMID: 22983580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activity of posaconazole in treatment of experimental disseminated zygomycosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 Nov;47(11):3647-50. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.11.3647-3650.2003. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. PMID: 14576138 Free PMC article.
-
Extra copies of the Aspergillus fumigatus squalene epoxidase gene confer resistance to terbinafine: genetic approach to studying gene dose-dependent resistance to antifungals in A. fumigatus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Jul;48(7):2490-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.7.2490-2496.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 15215099 Free PMC article.
-
Rhino-orbitocerebral mucormycosis caused by Apophysomyces elegans.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Mar;44(3):892-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.44.3.892-898.2006. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16517873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro susceptibilities of 217 clinical isolates of zygomycetes to conventional and new antifungal agents.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Jul;51(7):2587-90. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00452-07. Epub 2007 Apr 23. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17452481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corbel, M. J., and S. M. Eades. 1975. Factors determining the susceptibility of mice to experimental phycomycosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 8:551-564. - PubMed
-
- Corbel, M. J., and S. M. Eades. 1978. Observations on the localization of Absidia corymbifera in vivo. Sabouraudia 16:125-132. - PubMed
-
- Dannaoui, E., E. Borel, M. F. Monier, M. A. Piens, S. Picot, and F. Persat. 2001. Acquired itraconazole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 47:333-340. - PubMed
-
- Dannaoui, E., E. Borel, F. Persat, M. F. Monier, and M. A. Piens. 1999. In-vivo itraconazole resistance of Aspergillus fumigatus in systemic murine aspergillosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 48:1087-1093. - PubMed
-
- Dannaoui, E., E. Borel, F. Persat, M. A. Piens, and S. Picot. 2000. Amphotericin B resistance of Aspergillus terreus in a murine model of disseminated aspergillosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 49:601-606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

