Chromosome-encoded class D beta-lactamase OXA-23 in Proteus mirabilis
- PMID: 12019126
- PMCID: PMC127228
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.6.2004-2006.2002
Chromosome-encoded class D beta-lactamase OXA-23 in Proteus mirabilis
Abstract
Ten nonrepetitive Proteus mirabilis isolates, which were collected over 4 years (1996 to 1999) at the teaching hospital of Clermont-Ferrand, France, produced class D carbapenemase OXA-23. MICs of imipenem were 0.25 to 0.5 microg/ml for these clinical isolates. Molecular typing revealed that the 10 P. mirabilis isolates originated from the same clonal strain. Hybridization of I-CeuI-generated chromosome fragments with a bla(OXA-23) probe showed that the gene was chromosome encoded in the P. mirabilis strain.
Figures
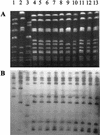
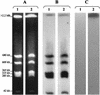
References
-
- Afzal-Shah, M., H. E. Villar, and D. M. Livermore. 1999. Biochemical characteristics of a carbapenemase from an Acinetobacter baumannii isolate collected in Buenos Aires, Argentina. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 43:127-131. - PubMed
-
- Bingen, E., C. Boissinot, P. Desjardins, H. Cave, N. Brahimi, N. Lambert-Zechovsky, E. Denamur, P. Blot, and J. Elion. 1993. Arbitrarily primed polymerase chain reaction provides rapid differentiation of Proteus mirabilis isolates from a pediatric hospital. J. Clin. Microbiol. 31:1055-1059. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

