Mutational analysis of the conserved cysteines of the rat P2X2 purinoceptor
- PMID: 12019306
- PMCID: PMC6757666
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-10-03873.2002
Mutational analysis of the conserved cysteines of the rat P2X2 purinoceptor
Abstract
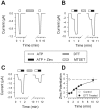
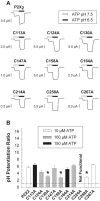
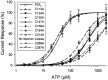
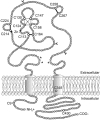
P2X receptors are ATP-gated cation channels that are widely expressed in the brain. The extracellular domains of all seven P2X receptors contain 10 conserved cysteines, which could form disulfide bonds or binding sites for transition metals that modulate P2X receptors. To test whether these cysteines are critical for receptor function, we studied wild-type rat P2X(2) receptors and 10 mutant P2X(2) receptors, each containing an alanine substituted for a cysteine. Nine mutants were functional but had reduced maximum currents compared with wild-type P2X(2) expressed in either Xenopus oocytes or human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells. The 10th mutant (C224A) did not respond to ATP when expressed in oocytes and gave very small currents in HEK 293 cells. Seven mutants (C113A, C124A, C130A, C147A, C158A, C164A, and C214A) showed rightward shifts (9- to 30-fold) in their ATP concentration-response relationships and very little potentiation by zinc. In contrast, C258A and C267A had EC(50) values similar to those of wild-type P2X(2) and were potentiated by zinc. Acidic pH potentiated wild-type and all mutant receptor currents. Despite the loss of zinc potentiation in seven mutants, these cysteines are unlikely to be exposed in the zinc-binding site, because [2-(trimethylammonium)ethyl] methanethiosulfonate bromide did not prevent zinc potentiation of wild-type receptor currents. On the basis of correlations in the maximum current, EC(50), zinc potentiation, and pH potentiation, we suggest that the following cysteine pairs form disulfide bonds: C113-C164, C214-C224, and C258-C267. We also suggest that C124, C130, C147, and C158 form two disulfide bonds, but we are unable to assign specific cysteine pairs to these two bonds.
Figures

References
-
- Acuna-Castillo C, Morales B, Huidobro-Toro JP. Zinc and copper modulate differentially the P2X4 receptor. J Neurochem. 2000;74:1529–1537. - PubMed
-
- Barnard EA, Simon J, Webb TE. Nucleotide receptors in the nervous system: an abundant component using diverse transduction mechanisms. Mol Neurobiol. 1997;15:103–129. - PubMed
-
- Brake AJ, Julius D. Signaling by extracellular nucleotides. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1996;12:519–541. - PubMed
-
- Brake AJ, Wagenbach MJ, Julius D. New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotropic ATP receptor. Nature. 1994;371:519–523. - PubMed
-
- Brooks SP, Storey KB. Bound and determined: a computer program for making buffers of defined ion concentrations. Anal Biochem. 1992;201:119–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
