Molecular aspects of primary immunodeficiencies: lessons from cytokine and other signaling pathways
- PMID: 12021239
- PMCID: PMC150986
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI15769
Molecular aspects of primary immunodeficiencies: lessons from cytokine and other signaling pathways
Figures
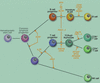
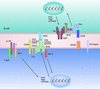
References
-
- Fischer A. Primary immunodeficiency diseases: an experimental model for molecular medicine. Lancet. 2001;357:1863–1869. - PubMed
-
- Buckley RH. Primary immunodeficiency diseases due to defects in lymphocytes. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1313–1324. - PubMed
-
- Noguchi M, et al. Interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain mutation results in X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency in humans. Cell. 1993;73:147–157. - PubMed
-
- Puel A, Ziegler SF, Buckley RH, Leonard WJ. Defective IL7R expression in T(-)B(+)NK(+) severe combined immunodeficiency. Nat Genet. 1998;20:394–397. - PubMed
-
- Macchi P, et al. Mutations of Jak-3 gene in patients with autosomal severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) Nature. 1995;377:65–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

