Regulation of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 activity by wild-type and mutant hepatitis B virus X proteins
- PMID: 12021320
- PMCID: PMC136206
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.12.5875-5881.2002
Regulation of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 activity by wild-type and mutant hepatitis B virus X proteins
Abstract
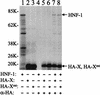
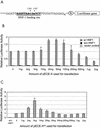
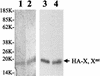
The hepatitis B virus (HBV) core promoter regulates the transcription of two related RNA products named precore RNA and core RNA. Previous studies indicate that a double-nucleotide mutation that occurs frequently during chronic HBV infection converts a nuclear receptor binding site in the core promoter to the binding site of the transcription factor hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 (HNF-1) and specifically suppresses the transcription of the precore RNA. This mutation also changes two codons in the overlapping X protein coding sequence. In this report, we demonstrate that the X protein and its mutant X(mt) can physically bind to HNF-1 both in vitro and in vivo. Further analyses indicate that both X and X(mt) can enhance the gene transactivation and the DNA binding activities of HNF-1. This finding demonstrates for the first time that the X protein can stimulate the DNA binding activity of a homeodomain transcription factor. Interestingly, while both X and X(mt) can stimulate the HNF-1 activities, they differ in their effects: a smaller amount of X(mt) is needed to generate greater transactivation and DNA binding activities of HNF-1. This functional difference between X and X(mt) may have important implications in HBV pathogenesis and is apparently why they have different effects on the core promoter bearing the HNF-1 binding site.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Regulation of hepatitis B virus core promoter by transcription factors HNF1 and HNF4 and the viral X protein.J Virol. 2004 Jul;78(13):6908-14. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.13.6908-6914.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15194767 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of suppression of hepatitis B virus precore RNA transcription by a frequent double mutation.J Virol. 1999 Feb;73(2):1239-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.2.1239-1244.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 9882327 Free PMC article.
-
A hepatitis B virus mutant with a new hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 binding site emerging in transplant-transmitted fulminant hepatitis B.Hepatology. 1997 Jun;25(6):1507-15. doi: 10.1002/hep.510250633. Hepatology. 1997. PMID: 9185776
-
Type-I protein-C deficiency caused by disruption of a hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF)-6/HNF-1 binding site in the human protein-C gene promoter.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1999 Apr-May;9(3-4):82-5. doi: 10.1016/s1050-1738(99)00010-9. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1999. PMID: 10578522 Review.
-
[Molecular background and clinical characteristics of autosomal dominant type 2 diabetes mellitus].Przegl Lek. 2000;57 Suppl 3:13-8. Przegl Lek. 2000. PMID: 11293229 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Hepatitis B Virus Promoter Region Mutations.Viruses. 2018 Nov 1;10(11):603. doi: 10.3390/v10110603. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30388827 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to Inhibit Hepatitis B Virus at the Transcript Level.Viruses. 2021 Jul 9;13(7):1327. doi: 10.3390/v13071327. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34372533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of hepatitis B virus core promoter by transcription factors HNF1 and HNF4 and the viral X protein.J Virol. 2004 Jul;78(13):6908-14. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.13.6908-6914.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15194767 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of HBxAg in hepatocellular carcinoma and its relationship with Fas/FasL system.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Dec;9(12):2671-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2671. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 14669310 Free PMC article.
-
(-)-Lariciresinol Isolated from the Roots of Isatis indigotica Fortune ex Lindl. Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus by Regulating Viral Transcription.Molecules. 2022 May 18;27(10):3223. doi: 10.3390/molecules27103223. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35630700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrisani, O. M., and S. Barnabas. 1999. The transcriptional function of the hepatitis B virus X protein and its role in hepatocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Oncol. 15:373-379. - PubMed
-
- Barnabas, S., T. Hai, and O. M. Andrisani. 1997. The hepatitis B virus X protein enhances the DNA binding potential and transcription efficacy of bZip transcription factors. J. Biol. Chem. 272:20684-20690. - PubMed
-
- Baumhueter, S., D. B. Mendel, P. B. Conley, C. J. Kuo, C. Turk, M. K. Graves, C. A. Edwards, G. Courtois, and G. R. Crabtree. 1990. HNF-1 shares three sequence motifs with the POU domain proteins and is identical to LF-B1 and APF. Genes Dev. 4:372-379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

