Effects of antiretroviral drugs on human immunodeficiency virus type 1-induced CD4(+) T-cell death
- PMID: 12021329
- PMCID: PMC136220
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.12.5966-5973.2002
Effects of antiretroviral drugs on human immunodeficiency virus type 1-induced CD4(+) T-cell death
Abstract
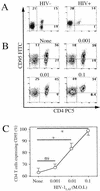
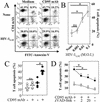
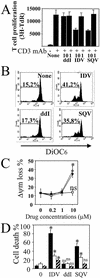
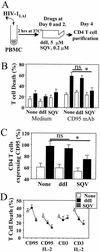
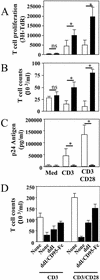
Apoptosis of peripheral blood T cells plays an important role in the pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. In this study, we found that HIV type 1 (HIV-1) primes CD4(+) T cells from healthy donors for apoptosis, which occurs after CD95 ligation or CD3-T-cell receptor (TCR) stimulation. CD95-mediated death did not depend on CD4 T-cell infection, since it occurred in the presence of the reverse transcriptase inhibitor didanosine (ddI). In contrast, apoptosis induced by productive infection (CD3-TCR stimulation) is prevented by both CD95 decoy receptor and ddI. Our data suggest that HIV-1 triggers at least two distinct death pathways: a CD95-dependent pathway that does not require viral replication and a viral replication-mediated cell death independent of the CD95 pathway. Further experiments indicated that saquinavir, a protease inhibitor, at a 0.2 microM concentration, decreased HIV-mediated CD95 expression and thus cell death, which is independent of its role in inhibiting viral replication. However, treatment of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from healthy donors with a higher concentration (10 microM) of an HIV protease inhibitor, saquinavir or indinavir, induced both a loss in mitochondrial membrane potential (DeltaPsim) and cell death. Thus, protease inhibitors have the potential for both beneficial and detrimental effects on CD4(+) T cells independent of their antiretroviral effects.
Figures
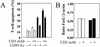
References
-
- Ameisen, J. C., J. Estaquier, and T. Idziorek. 1994. From AIDS to parasite infection: pathogen-mediated subversion of programmed cell death as a mechanism for immune dysregulation. Immunol. Rev. 142:9-51. - PubMed
-
- Amendola, A., F. Poccia, F. Martini, C. Gioia, V. Galati, M. Pierdominici, M. Marziali, F. Pandolfi, V. Colizzi, M. Piacentini, E. Girardi, G. D'Offizi, et al. 2000. Decreased CD95 expression on naive T cells from HIV-infected persons undergoing highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART) and the influence of IL-2 low dose administration. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 120:324-332. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andre, P., M. Groettrup, P. Klenerman, R. de Giuli, B. L. Booth, Jr., V. Cerundolo, M. Bonneville, F. Jotereau, R. M. Zinkernagel, and V. Lotteau. 1998. An inhibitor of HIV-1 protease modulates proteasome activity, antigen presentation, and T cell responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:13120-13124. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aries, S. P., K. Weyrich, B. Schaaf, F. Hansen, R. H. Dennin, and K. Dalhoff. 1998. Early T-cell apoptosis and Fas expression during antiretroviral therapy in individuals infected with human immunodeficiency virus-1. Scand. J. Immunol. 48:86-91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

