Site-directed spin labeling of a bacterial chemoreceptor reveals a dynamic, loosely packed transmembrane domain
- PMID: 12021446
- PMCID: PMC2373632
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.0202502
Site-directed spin labeling of a bacterial chemoreceptor reveals a dynamic, loosely packed transmembrane domain
Abstract
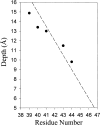
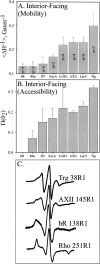
We used site-directed spin labeling and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy to investigate dynamics and helical packing in the four-helix transmembrane domain of the homodimeric bacterial chemoreceptor Trg. We focused on the first transmembrane helix, TM1, particularly on the nine-residue sequence nearest the periplasm, because patterns of disulfide formation between introduced cysteines had identified that segment as the region of closest approach among neighboring transmembrane helices. Along this sequence, mobility and accessibility of the introduced spin label were characteristic of loosely packed or solvent-exposed side chains. This was also the case for eight additional positions around the circumference and along the length of TM1. For the continuous nine-residue sequence near the periplasm, mobility and accessibility varied only modestly as a function of position. We conclude that side chains of TM1 that face the interior of the four-helix domain interact with neighboring helices but dynamic movement results in loose packing. Compared to transmembrane segments of other membrane proteins reconstituted into lipid bilayers and characterized by site-directed spin labeling, TM1 of chemoreceptor Trg is the most dynamic and loosely packed. A dynamic, loosely packed chemoreceptor domain can account for many experimental observations about the transmembrane domains of chemoreceptors.
Figures



References
-
- Almeida, F.C. and Opella, S.J. 1997. fd coat protein structure in membrane environments: Structural dynamics of the loop between the hydrophobic trans-membrane helix and the amphipathic in-plane helix. J. Mol. Biol. 270 481–495. - PubMed
-
- Altenbach, C., Cai, K., Khorana, H.G., and Hubbell, W.L. 1999. Structural features and light-dependent changes in the sequence 306–322 extending from helix VII to the palmitoylation sites in rhodopsin: A site-directed spin-labeling study. Biochemistry 38 7931–7937. - PubMed
-
- Altenbach, C., Marti, T., Khorana, H.G., and Hubbell, W.L. 1990. Transmembrane protein structure: Spin labeling of bacteriorhodopsin mutants. Science 248 1088–1092. - PubMed
-
- Altenbach, C., Oh, K.J., Trabanino, R.J., Hideg, K., and Hubbell, W.L. 2001. Estimation of inter-residue distances in spin labeled proteins at physiological temperatures: Experimental strategies and practical limitations. Biochemistry 40 15471–15482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

