TEM-1 beta-lactamase as a scaffold for protein recognition and assay
- PMID: 12021449
- PMCID: PMC2373628
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.0203102
TEM-1 beta-lactamase as a scaffold for protein recognition and assay
Abstract
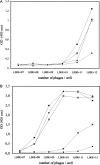
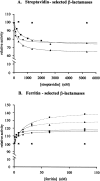
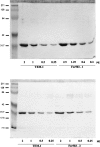
A large number of different proteins or protein domains have been investigated as possible scaffolds to engineer antibody-like molecules. We have previously shown that the TEM-1 beta-lactamase can accommodate insertions of random sequences in two loops surrounding its active site without compromising its activity. From the libraries that were generated, active enzymes binding with high affinities to monoclonal antibodies raised against prostate-specific antigen, a protein unrelated to beta-lactamase, could be isolated. Antibody binding was shown to affect markedly the enzyme activity. As a consequence, these enzymes have the potential to be used as signaling molecules in direct or competitive homogeneous immunoassay. Preliminary results showed that beta-lactamase clones binding to streptavidin could also be isolated, indicating that some enzymes in the libraries have the ability to recognize proteins other than antibodies. In this paper, we show that, in addition to beta-lactamases binding to streptavidin, beta-lactamase clones binding to horse spleen ferritin and beta-galactosidase could be isolated. Affinity maturation of a clone binding to ferritin allowed obtaining beta-lactamases with affinities comprised between 10 and 20 nM (Kd) for the protein. Contrary to what was observed for beta-lactamases issued from selections on antibodies, enzyme complexation induced only a modest effect on enzyme activity, in the three cases studied. This kind of enzyme could prove useful in replacement of enzyme-conjugated antibodies in enzyme-linked immunosorbant assays (ELISA) or in other applications that use antibodies conjugated to an enzyme.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Engineering a regulatable enzyme for homogeneous immunoassays.Nat Biotechnol. 1999 Jan;17(1):67-72. doi: 10.1038/5243. Nat Biotechnol. 1999. PMID: 9920272
-
Phage-displayed combinatorial peptide libraries in fusion to beta-lactamase as reporter for an accelerated clone screening: Potential uses of selected enzyme-linked affinity reagents in downstream applications.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2010 Jan;13(1):75-87. doi: 10.2174/138620710790218258. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2010. PMID: 20214576 Free PMC article.
-
Developing bifunctional beta-lactamase molecules with built-in target-recognizing module for prodrug therapy: identification of Enterobacter Cloacae P99 cephalosporinase loops suitable for randomization and phage-display selection.J Mol Recognit. 2009 Nov-Dec;22(6):425-36. doi: 10.1002/jmr.957. J Mol Recognit. 2009. PMID: 19437416 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of beta-lactamases and penicillin binding mutants from a library of phage displayed TEM-1 beta-lactamase randomly mutated in the active site omega-loop.J Mol Biol. 2000 Jan 21;295(3):527-40. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3376. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10623544
-
Dissecting the protein-protein interface between beta-lactamase inhibitory protein and class A beta-lactamases.J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 8;279(41):42860-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406157200. Epub 2004 Jul 28. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15284234
Cited by
-
A new generation of protein display scaffolds for molecular recognition.Protein Sci. 2006 Jan;15(1):14-27. doi: 10.1110/ps.051817606. Protein Sci. 2006. PMID: 16373474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spectroscopic analysis and docking simulation on the recognition and binding of TEM-1 β-lactamase with β-lactam antibiotics.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Oct;14(4):3288-3298. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4853. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28912880 Free PMC article.
-
Active TEM-1 beta-lactamase mutants with random peptides inserted in three contiguous surface loops.Protein Sci. 2006 Oct;15(10):2323-34. doi: 10.1110/ps.062303606. Epub 2006 Sep 8. Protein Sci. 2006. PMID: 16963643 Free PMC article.
-
Miniproteins as phage display-scaffolds for clinical applications.Molecules. 2011 Mar 14;16(3):2467-85. doi: 10.3390/molecules16032467. Molecules. 2011. PMID: 21407148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein scaffold-based molecular probes for cancer molecular imaging.Amino Acids. 2011 Nov;41(5):1037-47. doi: 10.1007/s00726-010-0503-9. Epub 2010 Feb 21. Amino Acids. 2011. PMID: 20174842 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benito, A., Feliu, J.X., and Villaverde, A. 1996. β-Galactosidase enzymatic activity as a molecular probe to detect specific antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 271 21251–21256. - PubMed
-
- Brennan, C., Christianson, K., Surowy, T., and Mandecki, W. 1994. Modulation of enzyme activity by antibody binding to an alkaline phosphatase-epitope hybrid protein. Protein Eng. 7 509–514. - PubMed
-
- Cadwell, R.C. and Joyce, G.F. 1994. Mutagenic PCR. PCR Methods Applic. 3 S136–S140. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

