Leukemia-associated Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor promotes G alpha q-coupled activation of RhoA
- PMID: 12024019
- PMCID: PMC133844
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.12.4053-4061.2002
Leukemia-associated Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor promotes G alpha q-coupled activation of RhoA
Abstract
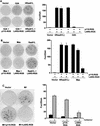
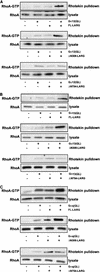
Leukemia-associated Rho guanine-nucleotide exchange factor (LARG) belongs to the subfamily of Dbl homology RhoGEF proteins (including p115 RhoGEF and PDZ-RhoGEF) that possess amino-terminal regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) boxes also found within GTPase-accelerating proteins (GAPs) for heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunits. p115 RhoGEF stimulates the intrinsic GTP hydrolysis activity of G alpha 12/13 subunits and acts as an effector for G13-coupled receptors by linking receptor activation to RhoA activation. The presence of RGS box and Dbl homology domains within LARG suggests this protein may also function as a GAP toward specific G alpha subunits and couple G alpha activation to RhoA-mediating signaling pathways. Unlike the RGS box of p115 RhoGEF, the RGS box of LARG interacts not only with G alpha 12 and G alpha 13 but also with G alpha q. In cellular coimmunoprecipitation studies, the LARG RGS box formed stable complexes with the transition state mimetic forms of G alpha q, G alpha 12, and G alpha 13. Expression of the LARG RGS box diminished the transforming activity of oncogenic G protein-coupled receptors (Mas, G2A, and m1-muscarinic cholinergic) coupled to G alpha q and G alpha 13. Activated G alpha q, as well as G alpha 12 and G alpha 13, cooperated with LARG and caused synergistic activation of RhoA, suggesting that all three G alpha subunits stimulate LARG-mediated activation of RhoA. Our findings suggest that the RhoA exchange factor LARG, unlike the related p115 RhoGEF and PDZ-RhoGEF proteins, can serve as an effector for Gq-coupled receptors, mediating their functional linkage to RhoA-dependent signaling pathways.
Figures
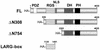

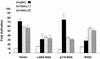

References
-
- Althoefer, H., P. Eversole-Cire, and M. I. Simon. 1997. Constitutively active Gαq and Gα13 trigger apoptosis through different pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 272:24380-24386. - PubMed
-
- Berman, D. M., T. Kozasa, and A. G. Gilman. 1996. The GTPase-activating protein RGS4 stabilizes the transition state for nucleotide hydrolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 271:27209-27212. - PubMed
-
- Buhl, A. M., N. L. Johnson, N. Dhanasekaran, and G. L. Johnson. 1995. Gα12 and Gα13 stimulate Rho-dependent stress fiber formation and focal adhesion assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 270:24631-24634. - PubMed
-
- Cerione, R. A., and Y. Zheng. 1996. The Dbl family of oncogenes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 8:216-222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
