The highly conserved TldD and TldE proteins of Escherichia coli are involved in microcin B17 processing and in CcdA degradation
- PMID: 12029038
- PMCID: PMC135094
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.12.3224-3231.2002
The highly conserved TldD and TldE proteins of Escherichia coli are involved in microcin B17 processing and in CcdA degradation
Abstract
Microcin B17 (MccB17) is a peptide antibiotic produced by Escherichia coli strains carrying the pMccB17 plasmid. MccB17 is synthesized as a precursor containing an amino-terminal leader peptide that is cleaved during maturation. Maturation requires the product of the chromosomal tldE (pmbA) gene. Mature microcin is exported across the cytoplasmic membrane by a dedicated ABC transporter. In sensitive cells, MccB17 targets the essential topoisomerase II DNA gyrase. Independently, tldE as well as tldD mutants were isolated as being resistant to CcdB, another natural poison of gyrase encoded by the ccd poison-antidote system of plasmid F. This led to the idea that TldD and TldE could regulate gyrase function. We present in vivo evidence supporting the hypothesis that TldD and TldE have proteolytic activity. We show that in bacterial mutants devoid of either TldD or TldE activity, the MccB17 precursor accumulates and is not exported. Similarly, in the ccd system, we found that TldD and TldE are involved in CcdA and CcdA41 antidote degradation rather than being involved in the CcdB resistance mechanism. Interestingly, sequence database comparisons revealed that these two proteins have homologues in eubacteria and archaebacteria, suggesting a broader physiological role.
Figures
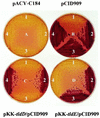

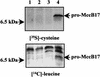

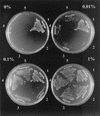

References
-
- Afif, H., N. Allali, M. Couturier, and L. Van Melderen. 2001. The ratio between CcdA and CcdB modulates the transcriptional repression of the ccd poison-antidote system. Mol. Microbiol. 41:73-82. - PubMed
-
- Bahassi, E. M., M. H. O'Dea, N. Allali, J. Messens, M. Gellert, and M. Couturier. 1999. Interactions of CcdB with DNA gyrase. Inactivation of Gyra, poisoning of the gyrase-DNA complex, and the antidote action of CcdA. J. Biol. Chem. 274:10936-10944. - PubMed
-
- Bernard, P., and M. Couturier. 1991. The 41 carboxy-terminal residues of the miniF plasmid CcdA protein are sufficient to antagonize the killer activity of the CcdB protein. Mol. Gen. Genet. 226:297-304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

