FpvA receptor involvement in pyoverdine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 12029043
- PMCID: PMC135083
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.12.3268-3275.2002
FpvA receptor involvement in pyoverdine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
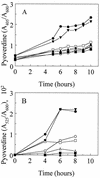
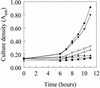
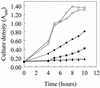
Alignment of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa ferric pyoverdine receptor, FpvA, with similar ferric-siderophore receptors revealed that the mature protein carries an extension of ca. 70 amino acids at its N terminus, an extension shared by the ferric pseudobactin receptors of P. putida. Deletion of fpvA from the chromosome of P. aeruginosa reduced pyoverdine production in this organism, as a result of a decline in expression of genes (e.g., pvdD) associated with the biosynthesis of the pyoverdine peptide moiety. Wild-type fpvA restored pvd expression in the mutant, thereby complementing its pyoverdine deficiency, although a deletion derivative of fpvA encoding a receptor lacking the N terminus of the mature protein did not. The truncated receptor was, however, functional in pyoverdine-mediated iron uptake, as evidenced by its ability to promote pyoverdine-dependent growth in an iron-restricted medium. These data are consistent with the idea that the N-terminal extension plays a role in FpvA-mediated pyoverdine biosynthesis in P. aeruginosa.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of type II and type III pyoverdine receptors from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Microbiology (Reading). 2003 Apr;149(Pt 4):821-831. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26136-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2003. PMID: 12686625
-
Pyoverdine-mediated regulation of FpvA synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: involvement of a probable extracytoplasmic-function sigma factor, FpvI.J Bacteriol. 2003 Feb;185(4):1261-5. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.4.1261-1265.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12562796 Free PMC article.
-
FpvB, an alternative type I ferripyoverdine receptor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Microbiology (Reading). 2004 Jun;150(Pt 6):1671-1680. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27035-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2004. PMID: 15184553
-
Structure-function relationships in the bifunctional ferrisiderophore FpvA receptor from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Biometals. 2009 Aug;22(4):671-8. doi: 10.1007/s10534-008-9203-2. Epub 2009 Jan 20. Biometals. 2009. PMID: 19153809 Review.
-
High affinity iron uptake by pyoverdine in Pseudomonas aeruginosa involves multiple regulators besides Fur, PvdS, and FpvI.Biometals. 2023 Apr;36(2):255-261. doi: 10.1007/s10534-022-00369-6. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Biometals. 2023. PMID: 35171432 Review.
Cited by
-
Ferric-pyoverdine recognition by Fpv outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas protegens Pf-5.J Bacteriol. 2013 Feb;195(4):765-76. doi: 10.1128/JB.01639-12. Epub 2012 Dec 7. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23222724 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium and magnesium enhance the production of Pseudomonas aeruginosa protease IV, a corneal virulence factor.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2005 Jan;194(1-2):39-45. doi: 10.1007/s00430-003-0207-9. Epub 2003 Nov 20. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 14628143
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa FpvB Is a High-Affinity Transporter for Xenosiderophores Ferrichrome and Ferrioxamine B.mBio. 2023 Feb 28;14(1):e0314922. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03149-22. Epub 2022 Dec 12. mBio. 2023. PMID: 36507834 Free PMC article.
-
FpvIR control of fpvA ferric pyoverdine receptor gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: demonstration of an interaction between FpvI and FpvR and identification of mutations in each compromising this interaction.J Bacteriol. 2005 Aug;187(16):5648-57. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.16.5648-5657.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 16077110 Free PMC article.
-
A gene network-driven approach to infer novel pathogenicity-associated genes: application to Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1.mSystems. 2023 Dec 21;8(6):e0047323. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00473-23. Epub 2023 Nov 3. mSystems. 2023. PMID: 37921470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angerer, A., S. Enz, M. Ochs, and V. Braun. 1995. Transcriptional regulation of ferric citrate transport in Escherichia coli K-12: Fecl belongs to a new subfamily of sigma 70-type factors that respond to extracytoplasmic stimuli. Mol. Microbiol. 18:163-174. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1992. Short protocols in molecular biology, 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, N.Y.
-
- Barton, H. A., Z. Johnson, A. I. Vasil, and M. L. Vasil. 1996. Ferric uptake regulator mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with distinct alterations in the iron-dependent repression of exotoxin A and siderophores in aerobic and microaerobic environments. Mol. Microbiol. 21:1001-1017. - PubMed
-
- Bitter, W., J. D. Marugg, L. A. de Weger, J. Tommassen, and P. J. Weisbeek. 1991. The ferric-pseudobactin receptor PupA of Pseudomonas putida: homology to TonB-dependent Escherichia coli receptors and specificity of the protein. Mol. Microbiol. 5:647-655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

