Identification of residues in TIP47 essential for Rab9 binding
- PMID: 12032303
- PMCID: PMC124251
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.112198799
Identification of residues in TIP47 essential for Rab9 binding
Abstract
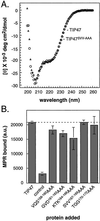
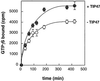
TIP47 (tail-interacting protein of 47 kDa) binds to the cytoplasmic domains of the cation-dependent and cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptors (MPRs) and is required for their transport from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network in vitro and in living cells. TIP47 recognizes distinct determinants in the cytoplasmic domains of these two receptors, and its ability to bind to the cation-independent MPR is enhanced by the concomitant binding of the Rab9 GTPase. We show here that TIP47 residues 161-169 are essential, but likely not sufficient, for Rab9 binding. Mutation of these residues led to a significant decrease in Rab9 binding, but did not alter the global folding of the protein. The most impaired mutant was indistinguishable from wild-type TIP47 in its circular dichroism spectrum, and mutant proteins that showed decreased Rab9 binding retained full capacity to bind to MPR cytoplasmic domains. Closely related sequences in a related protein, adipophilin, did not confer Rab9 binding capacity to that protein. Partial proteolysis of TIP47 and TIP47 mutant proteins revealed subtle conformational differences, suggesting that residues 161-169 reside in a portion of TIP47 that is important for its conformation. These experiments reveal distinct binding domains for the Rab9 GTPase and MPR cytoplasmic domains in the cargo selection protein TIP47.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Visualization of Rab9-mediated vesicle transport from endosomes to the trans-Golgi in living cells.J Cell Biol. 2002 Feb 4;156(3):511-8. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200109030. Epub 2002 Feb 4. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11827983 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Rab9 GTPase in facilitating receptor recruitment by TIP47.Science. 2001 May 18;292(5520):1373-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1056791. Science. 2001. PMID: 11359012
-
Purification and analysis of TIP47 function in Rab9-dependent mannose 6-phosphate receptor trafficking.Methods Enzymol. 2005;403:357-66. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)03031-4. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 16473602
-
[The double-play of PP17/TIP47].Med Sci (Paris). 2004 Nov;20(11):1020-5. doi: 10.1051/medsci/200420111020. Med Sci (Paris). 2004. PMID: 15525499 Review. French.
-
[Function of PAT family proteins in the lipid metabolism].Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2006 Apr;37(2):103-7. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2006. PMID: 16850611 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Rab9 GTPase is required for replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, filoviruses, and measles virus.J Virol. 2005 Sep;79(18):11742-51. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.18.11742-11751.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16140752 Free PMC article.
-
Rab9 GTPase regulates late endosome size and requires effector interaction for its stability.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Dec;15(12):5420-30. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-08-0747. Epub 2004 Sep 29. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15456905 Free PMC article.
-
Reevaluation of the requirement for TIP47 in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein incorporation.J Virol. 2013 Mar;87(6):3561-70. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03299-12. Epub 2013 Jan 16. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23325685 Free PMC article.
-
Rab11A controls the biogenesis of Birbeck granules by regulating Langerin recycling and stability.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Aug;18(8):3169-79. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-09-0779. Epub 2007 May 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17538027 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Rab GTPases in membrane traffic and cell physiology.Physiol Rev. 2011 Jan;91(1):119-49. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00059.2009. Physiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21248164 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

