Structure and function correlation in histone H2A peptide-mediated gene transfer
- PMID: 12032306
- PMCID: PMC124254
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.102168299
Structure and function correlation in histone H2A peptide-mediated gene transfer
Abstract
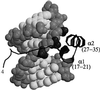
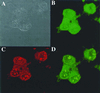
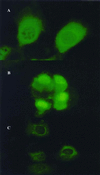
Histone H2A has been found to be efficient in DNA delivery into a number of cell lines. We have reasoned that this DNA-delivery activity is mediated by two mechanisms: (i) electrostatically driven DNA binding and condensation by histone and (ii) nuclear import of these histone H2A.DNA polyplexes via nuclear localization signals in the protein. We have identified a 37-aa N-terminal peptide of histone H2A that is active in in vitro gene transfer. This peptide can function as a nuclear localization signal and can bind DNA. Amino acid substitutions that replace positively charged residues and/or DNA-binding residues of this peptide obliterate transfection activity. The introduction of a proline in the first turn of an alpha-helix of this 37-mer obliterates transfection activity, suggesting that the integrity of the alpha-helical structure of the N-terminal region of histone H2A is related to its transfection activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Carassius auratus-originated recombinant histone H1 C-terminal peptide as gene delivery material.Biotechnol Prog. 2008 Jan-Feb;24(1):17-22. doi: 10.1021/bp070069b. Epub 2007 Jun 16. Biotechnol Prog. 2008. PMID: 17571853
-
Lysine residues in N-terminal and C-terminal regions of human histone H2A are targets for biotinylation by biotinidase.J Nutr Biochem. 2006 Apr;17(4):225-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2005.05.003. Epub 2005 Jun 8. J Nutr Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16109483 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of recombinant histones HMfA and HMfB from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Methanothermus fervidus.J Mol Biol. 2000 Oct 13;303(1):35-47. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4104. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 11021968
-
Histonefection: Novel and potent non-viral gene delivery.J Control Release. 2006 Jul 20;113(3):245-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.04.013. Epub 2006 Jun 27. J Control Release. 2006. PMID: 16806557 Review.
-
A comprehensive review on histone-mediated transfection for gene therapy.Biotechnol Adv. 2019 Jan-Feb;37(1):132-144. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.11.009. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Biotechnol Adv. 2019. PMID: 30472306 Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleosomes enter cells by clathrin- and caveolin-dependent endocytosis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Dec 2;49(21):12306-12319. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1121. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34865123 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of several Arabidopsis histone genes increases agrobacterium-mediated transformation and transgene expression in plants.Plant Cell. 2009 Oct;21(10):3350-67. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.070607. Epub 2009 Oct 9. Plant Cell. 2009. PMID: 19820187 Free PMC article.
-
A designer biomimetic vector with a chimeric architecture for targeted gene transfer.J Control Release. 2009 Jul 1;137(1):46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.03.005. Epub 2009 Mar 18. J Control Release. 2009. PMID: 19303038 Free PMC article.
-
Diseases originate and terminate by genes: unraveling nonviral gene delivery.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2013 Dec;3(6):593-610. doi: 10.1007/s13346-013-0159-6. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2013. PMID: 25786377
-
Efficient intracellular gene delivery using the formulation composed of poly (L-glutamic acid) grafted polyethylenimine and histone.Pharm Res. 2011 Apr;28(4):812-26. doi: 10.1007/s11095-010-0335-z. Epub 2010 Dec 14. Pharm Res. 2011. PMID: 21161337
References
-
- Balicki D, Beutler E. Medicine (Baltimore) 2002;81:69–86. - PubMed
-
- Felgner P L. Sci Am. 1997;276(6):102–106. - PubMed
-
- Felgner P L, Barenholz Y, Behr J P, Cheng S H, Cullis P, Huang L, Jessee J A, Seymour L, Szoka F, Thierry A R, et al. Hum Gene Ther. 1997;8:511–512. - PubMed
-
- Van Holde K E. Chromatin. New York: Springer; 1989.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

