Surface antigens of human embryonic stem cells: changes upon differentiation in culture
- PMID: 12033729
- PMCID: PMC1570685
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2002.00030.x
Surface antigens of human embryonic stem cells: changes upon differentiation in culture
Abstract
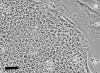
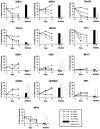
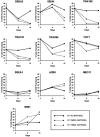
We have analysed the surface antigen phenotype of a human embryonic stem (hES) cell line (H7) and the changes that occur upon differentiation induced by retinoic acid, hexamethylene bisacetamide and dimethylsulphoxide. The undifferentiated stem cells expressed Stage Specific Embryonic Antigen-3 (SSEA3), SSEA4, TRA-1-60, and TRA-1-8 but not SSEA1. In these characteristics they closely resemble human embryonal carcinoma (EC) cells derived from testicular teratocarcinomas, and are distinct from murine EC and ES cells. The undifferentiated cells also expressed the liver/bone/kidney isozyme of alkaline phosphatase detected by antibody TRA-2-54, the class 1 major histocompatability antigens, HLA-ABC, and the human Thy1 antigen. Differentiation of hES cells was induced by retinoic acid, HMBA and DMSO with the appearance of various cell types including neurons and muscle cells. The surface antigens characteristically expressed by hES cells were down-regulated following induction of differentiation and other antigens appeared, notably several ganglioside glycolipids detected by antibodies VIN-IS-56 (GD3 and GD2), VIN-2PB-22 (GD2), A2B5 (GT3) and ME311 (9-O-acetyl-GD3). Whereas the expression of HLA was slightly down-regulated upon differentiation, its expression was strongly induced by interferon-y in both the undifferentiated and the differentiated cells, although the induction in the differentiated cultures was considerably stronger than in the stem cells. In all of these features the human ES cells, and their pattern of differentiation, resembled the pluripotent human EC cell line NTERA-2 although clearly the range of cells generated by the hES cells was considerably greater.
Figures

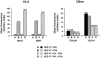
References
-
- Ackerman SL, Knowles BB, Andrews PW. Gene regulation during neuronal and non-neuronal differentiation of NTERA2 human teratocarcinoma-derived stem cells. Mol. Brain Res. 1994;200:157–162. - PubMed
-
- Andrews PW, Goodfellow PN. Antigen expression by somatic cell hybrids of a murine embryonal carcinoma cell with thymocytes and L cells. Somat. Cell Genet. 1980;6:271–284. - PubMed
-
- Andrews PW, Knowles BB, Goodfellow PN. A human cell surface antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody and controlled by a gene on chromosome 12. Somat. Cell Genet. 1981;7:435–443. - PubMed
-
- Andrews PW, Goodfellow PN, Shevinsky L, Bronson DL, Knowles BB. Cell surface antigens of a clonal human embryonal carcinoma cell line: Morphological and antigenic differentiation in culture. Int. J. Cancer. 1982;29:523–531. - PubMed
-
- Andrews PW. Retinoic acid induces neuronal differentiation of a cloned human embryonal carcinoma cell line in vitro. Dev. Biol. 1984;103:285–293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

