Vitamin D insufficiency among free-living healthy young adults
- PMID: 12034416
- PMCID: PMC3091001
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01091-4
Vitamin D insufficiency among free-living healthy young adults
Abstract
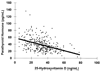
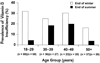
Long-term vitamin D insufficiency can cause secondary hyperparathyroidism and osteomalacia (1). In addition, there is increasing evidence that vitamin D may protect against common cancers, such as cancer of the colon (–4), prostate (5), and breast (6). Young adults aged 17 to 35 years drink inadequate amounts of milk (7) and are concerned about exposure to the sun because of the fear of developing skin cancer (8,9), which increases the risk of vitamin D insufficiency (10). We sought to examine the prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency in a group of free-living healthy young adults, consisting of mostly health care professionals, in Boston, Massachusetts.
Figures

References
-
- Adams JS, Kantorovich V, Wu C, et al. Resolution of vitamin D insufficiency in osteopenic patients results in rapid recovery of bone mineral density. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999;84:2729–2730. - PubMed
-
- Garland CF, Comstock GW, Garland FC, et al. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and colon cancer: eight-year prospective study. Lancet. 1989;2:1176–1178. - PubMed
-
- Tangpricha V, Flanagan JN, Whitlatch LW, et al. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-1α-hydroxylase in normal and malignant colon tissue. Lancet. 2001;357:1673–1674. - PubMed
-
- Cross HS, Bareis P, Hofer H, et al. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-1α-hydroxylase and vitamin D receptor gene expression in human colonic mucosa is elevated during early cancerogenesis. Steroids. 2001;66:287–292. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz GG, Hulka BS. Is vitamin D deficiency a risk factor for prostate cancer? (Hypothesis) Anticancer Res. 1990;10:1307–1311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

