The cell wall hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein RSH is essential for normal embryo development in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 12034904
- PMCID: PMC150614
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.010477
The cell wall hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein RSH is essential for normal embryo development in Arabidopsis
Abstract
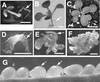
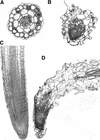
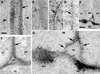
Although a large number of embryo mutants have been studied, mostly at the morphological level, the critical molecular and cellular events responsible for embryogenesis are unknown. Here, we report that using an enhancer-trap embryo mutant of Arabidopsis, we identified a gene, ROOT-SHOOT-HYPOCOTYL-DEFECTIVE (RSH), that is essential for the correct positioning of the cell plate during cytokinesis in cells of the developing embryo. We traced the earliest point of influence of RSH to the first asymmetrical division of the zygote. Homozygous rsh embryos were defective morphologically, had irregular cell shape and size, and germinated to form agravitropic-defective seedlings incapable of further development. The RSH gene encodes a Hyp-rich glycoprotein-type cell wall protein. RSH localized to the cell wall throughout the embryo and to a few well-defined postembryonic sites. Although several lines of evidence from previous work suggest that the cell wall is involved in development, the protein(s) involved remained elusive.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Self-assembly of the plant cell wall requires an extensin scaffold.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Feb 12;105(6):2226-31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0711980105. Epub 2008 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18256186 Free PMC article.
-
The hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein domain of the Arabidopsis LRX1 requires Tyr for function but not for insolubilization in the cell wall.Plant J. 2010 Aug;63(4):662-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04270.x. Plant J. 2010. PMID: 20545889
-
Delayed embryo development in the ARABIDOPSIS TREHALOSE-6-PHOSPHATE SYNTHASE 1 mutant is associated with altered cell wall structure, decreased cell division and starch accumulation.Plant J. 2006 Apr;46(1):69-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02662.x. Plant J. 2006. PMID: 16553896
-
TANMEI/EMB2757 encodes a WD repeat protein required for embryo development in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2005 Sep;139(1):163-73. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.060467. Epub 2005 Aug 19. Plant Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16113228 Free PMC article.
-
The asymmetric division of the Arabidopsis zygote: from cell polarity to an embryo axis.Sex Plant Reprod. 2011 Jun;24(2):161-9. doi: 10.1007/s00497-010-0160-x. Epub 2011 Jan 12. Sex Plant Reprod. 2011. PMID: 21225434 Review.
Cited by
-
The unusual Arabidopsis extensin gene atExt1 is expressed throughout plant development and is induced by a variety of biotic and abiotic stresses.Planta. 2003 Jul;217(3):356-66. doi: 10.1007/s00425-003-1002-y. Epub 2003 Mar 11. Planta. 2003. PMID: 14520562
-
Developmental localization and the role of hydroxyproline rich glycoproteins during somatic embryogenesis of banana (Musa spp. AAA).BMC Plant Biol. 2011 Feb 24;11:38. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-11-38. BMC Plant Biol. 2011. PMID: 21349190 Free PMC article.
-
Complementarity of medium-throughput in situ RNA hybridization and tissue-specific transcriptomics: case study of Arabidopsis seed development kinetics.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 20;6:24644. doi: 10.1038/srep24644. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27095274 Free PMC article.
-
Immunolocalization of cell wall polymers in grapevine (Vitis vinifera) internodes under nitrogen, phosphorus or sulfur deficiency.J Plant Res. 2016 Nov;129(6):1151-1163. doi: 10.1007/s10265-016-0851-y. Epub 2016 Jul 14. J Plant Res. 2016. PMID: 27417099
-
Emerging Functions for Cell Wall Polysaccharides Accumulated during Eudicot Seed Development.Plants (Basel). 2018 Sep 29;7(4):81. doi: 10.3390/plants7040081. Plants (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30274256 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ausubel, F.M., Brent, R., Kingston, R.E., Moore, D.D., Seidman, J.G., Smith, J.A., and Struhl, K. (1995). Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. (New York: John Wiley & Sons).
-
- Belanger, K., and Quatrano, R.S. (2000). Polarity: The role of localized secretion. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 3, 67–72. - PubMed
-
- Berger, F., Taylor, A., and Brownlee, C. (1994). Cell fate determination by the cell wall in early Fucus development. Science 263, 1421–1423. - PubMed
-
- Braam, J. (1999). If walls could talk. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2, 521–524. - PubMed
-
- Brownlee, C., and Bouget, F. (1998). Polarity determination in Fucus: From zygote to multicellular embryo. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 179–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

