Population diversity of Staphylococcus intermedius isolates from various host species: typing by 16S-23S intergenic ribosomal DNA spacer polymorphism analysis
- PMID: 12037109
- PMCID: PMC130735
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.6.2275-2277.2002
Population diversity of Staphylococcus intermedius isolates from various host species: typing by 16S-23S intergenic ribosomal DNA spacer polymorphism analysis
Abstract
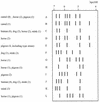
Twelve 16S-23S ribosomal DNA intergenic spacer (ITS-PCR) types were identified among 57 Staphylococcus intermedius isolates from humans and other animals. Six ITS-PCR types were host specific, and most human and canine strains belonged to the same types (A and J). Pigeon, horse, and mink strains appeared more heterogeneous.
Figures
References
-
- Aarestrup, F. M. 2001. Comparative ribotyping of Staphylococcus intermedius isolated from members of the Canoidea gives possible evidence for host-specificity and co-evolution of bacteria and hosts. Int. J. Syst. E vol. Microbiol. 51:1343-1347. - PubMed
-
- Allaker, R., N. Garrett, L. Kent, W. Noble, and D. Lloyd. 1993. Characterisation of Staphylococcus intermedius isolates from canine pyoderma and from healthy carriers by SDS-PAGE of exoproteins, immunoblotting and restriction endonuclease digest analysis. J. Med. Microbiol. 39:429-433. - PubMed
-
- Barrs, V., D. Briscoe, R. Malik, and D. Love. 2000. Use of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis to distinguish clinically important strains of Staphylococcus intermedius from the skin of dogs. Aust. Vet. J. 78:267-272. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases