An Otx-related homeodomain protein binds an LHbeta promoter element important for activation during gonadotrope maturation
- PMID: 12040015
- PMCID: PMC2932471
- DOI: 10.1210/mend.16.6.0841
An Otx-related homeodomain protein binds an LHbeta promoter element important for activation during gonadotrope maturation
Abstract
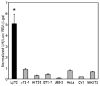
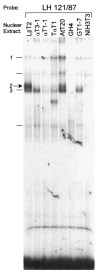
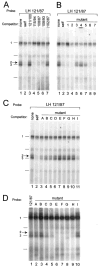
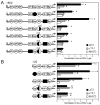
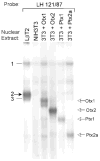
The hormone-secreting cell types of the anterior pituitary differentiate in a specific spatial and temporal manner. The alpha-subunit of the glycoprotein hormones appears at embryonic d 11.5 in the mouse, followed by steroidogenic factor-1, which distinguishes the gonadotrope progenitor cells, around embryonic d 14. Gonadotrope maturation is marked by the onset of LHbeta-gene expression 2 d later. The alphaT3-1 and LbetaT2 immortalized mouse pituitary cell lines correspond to these later sequential stages of gonadotrope differentiation. In addition to the early markers of the gonadotrope lineage present in alphaT3-1 cells, LbetaT2 cells also express markers of a mature gonadotrope, including LHbeta and FSHbeta. Using transient transfections to compare expression among gonadotrope and nongonadotrope-derived cell types, we show that the rat 1.8-kb LHbeta promoter directs reporter gene expression specifically to the mature gonadotrope LbetaT2 cell line. Promoter truncation and mutagenesis analyses indicate that the homeodomain (HD) element located at approximately -100 bp relative to the transcriptional start site is essential for this selectivity to LbetaT2 cells when compared with alphaT3-1 cells. In EMSAs, this HD site binds a protein present in LbetaT2 but not other gonadotrope-derived cells. Antibody supershift and competition experiments indicate that this LbetaT2 nuclear protein is a K50 HD protein related to the Otx family, though it is not a known pituitary homeobox transcription factor protein. These studies indicate a role for a novel Otx-related HD protein in gonadotrope maturation during development.
Figures


References
-
- Pierce JG, Parsons TF. Glycoprotein hormones: structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:465–495. - PubMed
-
- Alarid ET, Windle JJ, Whyte DB, Mellon PL. Immortalization of pituitary cells at discrete stages of development by directed oncogenesis in transgenic mice. Development. 1996;122:3319–3329. - PubMed
-
- Graham KE, Nusser KD, Low MJ. LβT2 gonadotroph cells secrete follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) in response to activin A. J Endocrinol. 1999;162:R1–R5. - PubMed
-
- Pernasetti F, Vasilyev VV, Rosenberg SB, Bailey JS, Huang H-J, Miller WL, Mellon PL. Cell-specific transcriptional regulation of FSHβ by activin and GnRH in the LβT2 pituitary gonadotrope cell model. Endocrinology. 2001;142:2284–2295. - PubMed
-
- Halvorson LM, Ito M, Jameson JL, Chin WW. Steroidogenic factor-1 and early growth response protein 1 act through two composite DNA binding sites to regulate luteinizing hormone β-subunit gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:14712–14720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

