CASK participates in alternative tripartite complexes in which Mint 1 competes for binding with caskin 1, a novel CASK-binding protein
- PMID: 12040031
- PMCID: PMC6758797
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-11-04264.2002
CASK participates in alternative tripartite complexes in which Mint 1 competes for binding with caskin 1, a novel CASK-binding protein
Abstract
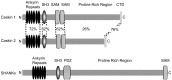
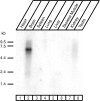
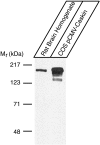
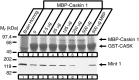
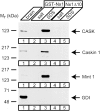
CASK, an adaptor protein of the plasma membrane, is composed of an N-terminal calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein (CaM) kinase domain, central PSD-95, Dlg, and ZO-1/2 domain (PDZ) and Src homology 3 (SH3) domains, and a C-terminal guanylate kinase sequence. The CaM kinase domain of CASK binds to Mint 1, and the region between the CaM kinase and PDZ domains interacts with Velis, resulting in a tight tripartite complex. CASK, Velis, and Mint 1 are evolutionarily conserved in Caenorhabditis elegans, in which homologous genes (called lin-2, lin-7, and lin-10) are required for vulva development. We now demonstrate that the N-terminal CaM kinase domain of CASK binds to a novel brain-specific adaptor protein called Caskin 1. Caskin 1 and a closely related isoform, Caskin 2, are multidomain proteins containing six N-terminal ankyrin repeats, a single SH3 domain, and two sterile alpha motif domains followed by a long proline-rich sequence and a short conserved C-terminal domain. Unlike CASK and Mint 1, no Caskin homolog was detected in C. elegans. Immunoprecipitations showed that Caskin 1, like Mint 1, is stably bound to CASK in the brain. Affinity chromatography experiments demonstrated that Caskin 1 coassembles with CASK on the immobilized cytoplasmic tail of neurexin 1, suggesting that CASK and Caskin 1 coat the cytoplasmic tails of neurexins and other cell-surface proteins. Detailed mapping studies revealed that Caskin 1 and Mint 1 bind to the same site on the N-terminal CaM kinase domain of CASK and compete with each other for CASK binding. Our data suggest that in the vertebrate brain, CASK and Velis form alternative tripartite complexes with either Mint 1 or Caskin 1 that may couple CASK to distinct downstream effectors.
Figures







References
-
- Biederer T, Südhof TC. Mints as adaptors: direct binding to neurexins and recruitment of munc18. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:39803–39806. - PubMed
-
- Biederer T, Südhof TC. Cask and protein 4.1 support F-actin nucleation on neurexins. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:47869–47876. - PubMed
-
- Borg JP, Yang Y, De Taddeo-Borg M, Margolis B, Turner RS. The X11alpha protein slows cellular amyloid precursor protein processing and reduces Abeta40 and Abeta42 secretion. J Biol Chem. 1998a;273:14761–14766. - PubMed
-
- Borg JP, Straight SW, Kaech SM, de Taddeo-Borg M, Kroon DE, Karnak D, Turner RS, Kim SK, Margolis B. Identification of an evolutionarily conserved heterotrimeric protein complex involved in protein targeting. J Biol Chem. 1998b;273:31633–31636. - PubMed
-
- Butz S, Okamoto M, Südhof TC. A tripartite protein complex with the potential to couple synaptic vesicle exocytosis to cell adhesion in brain. Cell. 1998;94:773–782. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
