Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabinol activate capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves via a CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptor-independent mechanism
- PMID: 12040079
- PMCID: PMC6758782
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-11-04720.2002
Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabinol activate capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves via a CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptor-independent mechanism
Abstract
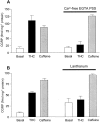
Although Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) produces analgesia, its effects on nociceptive primary afferents are unknown. These neurons participate not only in pain signaling but also in the local response to tissue injury. Here, we show that THC and cannabinol induce a CB(1)/CB(2) cannabinoid receptor-independent release of calcitonin gene-related peptide from capsaicin-sensitive perivascular sensory nerves. Other psychotropic cannabinoids cannot mimic this action. The vanilloid receptor antagonist ruthenium red abolishes the responses to THC and cannabinol. However, the effect of THC on sensory nerves is intact in vanilloid receptor subtype 1 gene knock-out mice. The THC response depends on extracellular calcium but does not involve known voltage-operated calcium channels, glutamate receptors, or protein kinases A and C. These results may indicate the presence of a novel cannabinoid receptor/ion channel in the pain pathway.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol inhibits electrically-evoked CGRP release and capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurogenic vasodilatation in the rat mesenteric arterial bed.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Nov;152(5):709-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707448. Epub 2007 Sep 10. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17828286 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoid inhibition of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurotransmission in the rat mesenteric arterial bed.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Apr 20;418(1-2):117-25. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)00940-2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11334873
-
Cannabinoid activation of recombinant and endogenous vanilloid receptors.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Jul 27;424(3):211-9. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01153-0. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11672565
-
Possible mechanisms of cannabinoid-induced antinociception in the spinal cord.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Oct 19;429(1-3):93-100. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01309-7. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11698030 Review.
-
Cannabinoid modulation of sensory neurotransmission via cannabinoid and vanilloid receptors: roles in regulation of cardiovascular function.Life Sci. 2002 Oct 18;71(22):2577-94. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(02)02086-6. Life Sci. 2002. PMID: 12354577 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence that the plant cannabinoid Delta9-tetrahydrocannabivarin is a cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptor antagonist.Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Dec;146(7):917-26. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706414. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16205722 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the In Vivo Haemodynamic Effects of Δ⁸-Tetrahydrocannabinol.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018 Jan 31;11(1):13. doi: 10.3390/ph11010013. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29385080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Receptors and channels targeted by synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists and antagonists.Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(14):1360-81. doi: 10.2174/092986710790980050. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20166927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-CB1, non-CB2 receptors for endocannabinoids, plant cannabinoids, and synthetic cannabimimetics: focus on G-protein-coupled receptors and transient receptor potential channels.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010 Mar;5(1):103-21. doi: 10.1007/s11481-009-9177-z. Epub 2009 Oct 22. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19847654 Review.
-
The complexities of the cardiovascular actions of cannabinoids.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 May;142(1):20-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705725. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15131000 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amann R, Maggi CA. Ruthenium red as a capsaicin antagonist. Life Sci. 1991;49:849–856. - PubMed
-
- Barber LA, Vasko MR. Activation of protein kinase C augments peptide release from rat sensory neurons. J Neurochem. 1996;67:72–80. - PubMed
-
- Bisogno T, Hanus L, De Petrocellis L, Tchilibon S, Ponde DE, Brandi I, Moriello AS, Davis JB, Mechoulam R, Di Marzo V. Molecular targets for cannabidiol and its synthetic analogues: effect on vanilloid VR1 receptors and on the cellular uptake and enzymatic hydrolysis of anandamide. Br J Pharmacol. 2001;134:845–852. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blumberg PM. In vitro studies on the mode of action of the phorbol esters, potent tumor promoters: part 1. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1980;8:153–197. - PubMed
-
- Burstein SH. The cannabinoid acids: nonpsychoactive derivatives with therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Ther. 1999;82:87–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
