T antigens of simian virus 40: molecular chaperones for viral replication and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 12040123
- PMCID: PMC120785
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.66.2.179-202.2002
T antigens of simian virus 40: molecular chaperones for viral replication and tumorigenesis
Abstract
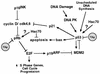
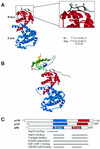
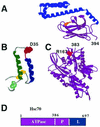
Simian virus 40 (SV40) is a small DNA tumor virus that has been extensively characterized due to its relatively simple genetic organization and the ease with which its genome is manipulated. The large and small tumor antigens (T antigens) are the major regulatory proteins encoded by SV40. Large T antigen is responsible for both viral and cellular transcriptional regulation, virion assembly, viral DNA replication, and alteration of the cell cycle. Deciphering how a single protein can perform such numerous and diverse functions has remained elusive. Recently it was established that the SV40 T antigens, including large T antigen, are molecular chaperones, each with a functioning DnaJ domain. The molecular chaperones were originally identified as bacterial genes essential for bacteriophage growth and have since been shown to be conserved in eukaryotes, participating in an array of both viral and cellular processes. This review discusses the mechanisms of DnaJ/Hsc70 interactions and how they are used by T antigen to control viral replication and tumorigenesis. The use of the DnaJ/Hsc70 system by SV40 and other viruses suggests an important role for these molecular chaperones in the regulation of the mammalian cell cycle and sheds light on the enigmatic SV40 T antigen-a most amazing molecule.
Figures
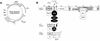
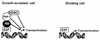

References
-
- Avantaggiati, M. L., V. Ogryzko, K. Gardner, A. Giordano, A. S. Levine, and K. Kelly. 1997. Recruitment of p300/CBP in p53-dependent signal pathways. Cell 89:1175-1184. - PubMed
-
- Bakkenist, C. J., J. Koreth, C. S. Williams, N. C. Hunt, and J. O. McGee. 1999. Heat shock cognate 70 mutations in sporadic breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 59:4219-4221. - PubMed
-
- Ballinger, C. A., P. Connell, Y. Wu, Z. Hu, L. J. Thompson, L. Y. Yin, and C. Patterson. 1999. Identification of CHIP, a novel tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein that interacts with heat shock proteins and negatively regulates chaperone functions. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19:4535-4545. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Banecki, B., and M. Zylicz. 1996. Real time kinetics of the DnaK/DnaJ/GrpE molecular chaperone machine action. J. Biol. Chem. 271:6137-6143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

