Potassium channels Kv1.1, Kv1.2 and Kv1.6 influence excitability of rat visceral sensory neurons
- PMID: 12042352
- PMCID: PMC2290329
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.018333
Potassium channels Kv1.1, Kv1.2 and Kv1.6 influence excitability of rat visceral sensory neurons
Abstract
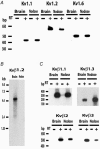
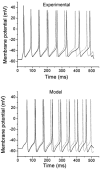
Voltage-gated potassium channels, Kv1.1, Kv1.2 and Kv1.6, were identified as PCR products from mRNA prepared from nodose ganglia. Immunocytochemical studies demonstrated expression of the proteins in all neurons from ganglia of neonatal animals (postnatal days 0-3) and in 85-90 % of the neurons from older animals (postnatal days 21-60). In voltage clamp studies, alpha-dendrotoxin (alpha-DTX), a toxin with high specificity for these members of the Kv1 family, was used to examine their contribution to K(+) currents of the sensory neurons. alpha-DTX blocked current in both A- and C-type neurons. The current had characteristics of a delayed rectifier with activation positive to -50 mV and little inactivation during 250 ms pulses. In current-clamp experiments alpha-DTX, used to eliminate the current, had no effect on resting membrane potential and only small effects on the amplitude and duration of the action potential of A- and C-type neurons. However, there were prominent effects on excitability. alpha-DTX lowered the threshold for initiation of discharge in response to depolarizing current steps, reduced spike after-hyperpolarization and increased the frequency/pattern of discharge of A- and C-type neurons at membrane potentials above threshold. Model simulations were consistent with these experimental results and demonstrated how the other major K(+) currents function in response to the loss of the alpha-DTX-sensitive current to effect these changes in action potential wave shape and discharge.
Figures


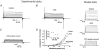
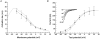
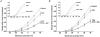



Similar articles
-
Kv1.2-containing K+ channels regulate subthreshold excitability of striatal medium spiny neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2004 Mar;91(3):1337-49. doi: 10.1152/jn.00414.2003. Epub 2003 Sep 17. J Neurophysiol. 2004. PMID: 13679409
-
Hyperexcitability and reduced low threshold potassium currents in auditory neurons of mice lacking the channel subunit Kv1.1.J Physiol. 2003 Apr 1;548(Pt 1):1-20. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.035568. Epub 2003 Feb 28. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12611922 Free PMC article.
-
Dendrotoxin-sensitive K(+) currents contribute to accommodation in murine spiral ganglion neurons.J Physiol. 2002 Aug 1;542(Pt 3):763-78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.017202. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12154177 Free PMC article.
-
The real life of voltage-gated K+ channels: more than model behaviour.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1997 Dec;18(12):474-83. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(97)01140-1. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1997. PMID: 9458696 Review.
-
Progress in Research of KV1.1 and KV1.3 Channels as Therapeutic Targets.Curr Top Med Chem. 2016;16(16):1877-85. doi: 10.2174/1568026616666160315142920. Curr Top Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26975504 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential distribution and function of hyperpolarization-activated channels in sensory neurons and mechanosensitive fibers.J Neurosci. 2004 Mar 31;24(13):3335-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5156-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15056713 Free PMC article.
-
KV 1/D-type potassium channels inhibit the excitability of bronchopulmonary vagal afferent nerves.J Physiol. 2022 Jun;600(12):2953-2971. doi: 10.1113/JP282803. Epub 2022 Apr 29. J Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35430729 Free PMC article.
-
μ-Opioid Receptor Activation Directly Modulates Intrinsically Photosensitive Retinal Ganglion Cells.Neuroscience. 2019 Jun 1;408:400-417. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.04.005. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 30981862 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-botulism triterpenoid toosendanin elicits calcium increase and exocytosis in rat sensory neurons.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2011 Nov;31(8):1151-62. doi: 10.1007/s10571-011-9716-z. Epub 2011 Jun 9. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21656151 Free PMC article.
-
De novo KCNA6 variants with attenuated KV 1.6 channel deactivation in patients with epilepsy.Epilepsia. 2023 Feb;64(2):443-455. doi: 10.1111/epi.17455. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Epilepsia. 2023. PMID: 36318112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amir R, Devor M. Functional cross-excitation between afferent A- and C-neurons in dorsal root ganglia. Neuroscience. 2000;95:189–195. - PubMed
-
- Bertoli A, Moran O, Conti F. Activation and deactivation properties of rat brain K channels of the Shaker-related family. European Biophysical Journal. 1994;23:379–384. - PubMed
-
- Christie MJ, Adelman JP, Douglass J, North RA. Expression of a cloned rat brain potassium channel in xenopous oocytes. Science. 1989;244:221–224. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

