Reduction of high-frequency network oscillations (ripples) and pathological network discharges in hippocampal slices from connexin 36-deficient mice
- PMID: 12042356
- PMCID: PMC2290340
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.017624
Reduction of high-frequency network oscillations (ripples) and pathological network discharges in hippocampal slices from connexin 36-deficient mice
Abstract
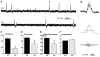
Recent evidence suggests that electrotonic coupling is an important mechanism for neuronal synchronisation in the mammalian cortex and hippocampus. Various types of network oscillations have been shown to depend on, or be sharpened by, gap junctions between inhibitory interneurones or excitatory projection cells. Here we made use of a targeted disruption of the gene coding for Cx36, a recently discovered neuronal gap junction subunit, to analyse its role in hippocampal network behaviour. Mice lacking Cx36 are viable and lack obvious morphological or behavioural abnormalities. Stimulation of afferent and efferent fibre pathways in hippocampal slices revealed a largely normal function of the synaptic circuitry, including tetanically evoked network oscillations. Spontaneous sharp waves and ripple (approximately 200 Hz) oscillations, however, occurred less frequently in slices from Cx36 -/- mice, and ripples were slightly slower than in littermate controls. Moreover, epileptiform discharges elicited by 4-aminopyridine were attenuated in slices from Cx36 -/- mice. Our findings indicate that Cx36 plays a role in the generation of certain forms of network synchronisation in the hippocampus, namely sharp wave-ripple complexes and hypersynchronous epileptiform discharges.
Figures

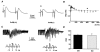
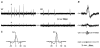
Similar articles
-
Sharp wave-like activity in the hippocampus in vitro in mice lacking the gap junction protein connexin 36.J Neurophysiol. 2003 Apr;89(4):2046-54. doi: 10.1152/jn.00549.2002. J Neurophysiol. 2003. PMID: 12686578
-
Cellular and network mechanisms underlying spontaneous sharp wave-ripple complexes in mouse hippocampal slices.J Physiol. 2003 Aug 1;550(Pt 3):873-87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.044602. Epub 2003 Jun 13. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12807984 Free PMC article.
-
Nonspecific effects of the gap junction blocker mefloquine on fast hippocampal network oscillations in the adult rat in vitro.Neuroscience. 2011 Sep 29;192:11-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.07.015. Epub 2011 Jul 14. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21763755
-
Axonal gap junctions between principal neurons: a novel source of network oscillations, and perhaps epileptogenesis.Rev Neurosci. 2002;13(1):1-30. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2002.13.1.1. Rev Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12013024 Review.
-
[Hippocampal ripple oscillations (200 Hz) in mechanisms of memory consolidation].Usp Fiziol Nauk. 2002 Oct-Dec;33(4):34-42. Usp Fiziol Nauk. 2002. PMID: 12449805 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
The role of Cx36 and Cx43 in 4-aminopyridine-induced rhythmic activity in the spinal nociceptive dorsal horn: an electrophysiological study in vitro.Physiol Rep. 2016 Jul;4(14):e12852. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12852. Physiol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27462070 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Connexins 30, 36, and 43 in Brain Tumors, Neurodegenerative Diseases, and Neuroprotection.Cells. 2020 Mar 31;9(4):846. doi: 10.3390/cells9040846. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32244528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reciprocal regulation of epileptiform neuronal oscillations and electrical synapses in the rat hippocampus.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 9;9(10):e109149. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109149. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25299405 Free PMC article.
-
Control of sleep and wakefulness.Physiol Rev. 2012 Jul;92(3):1087-187. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00032.2011. Physiol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22811426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential antiepileptogenic effect of neuronal Cx36 gap junction channel blockage.Transl Neurosci. 2021 Jan 22;12(1):46-51. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2021-0008. eCollection 2021 Jan 1. Transl Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33604079 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Avoli M. GABA-mediated synchronous potentials and seizure generation. Epilepsia. 1996;37:1035–1042. - PubMed
-
- Buzsáki G. Hippocampal sharp waves: their origin and significance. Brain Research. 1986;398:242–252. - PubMed
-
- Buzsáki G, Horváth Z, Urioste R, Hetke J, Wise K. High-frequency network oscillation in the hippocampus. Science. 1992;256:1025–1027. - PubMed
-
- Condorelli DF, Belluardo N, Trovato-Salinaro A, Mudo G. Expression of Cx36 in mammalian neurons. Brain Research Reviews. 2000;32:72–85. - PubMed
-
- Condorelli DF, Parenti R, Spinella F, Trovato Salinaro A, Belluardo N, Cardile V, Cicirata F. Cloning of a new gap junction gene (Cx36) highly expressed in mammalian brain neurons. European Journal of Neuroscience. 1998;10:1202–1208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

