Polypeptide hormones
- PMID: 12045281
- PMCID: PMC151259
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.010484
Polypeptide hormones
Figures
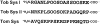




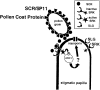
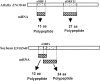
References
-
- Banting, F.G., and Best, C.H. (1922). The internal secretions of the pancreas. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 5 251–266.
-
- Bateman, A.J. (1955). Self-incompatibility systems in angiosperms, III. Crucifera. Heredity 9 52–68.
-
- Bourbonnais, Y., Germain, D., Lathcinian-Sadek, L., Boileau, G., and Thomas, D.Y. (1991). Prohormone processing by yeast proteases. Enzyme 45 244–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

