Rapid screening mitochondrial DNA mutation by using denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography
- PMID: 12046063
- PMCID: PMC4656414
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i3.426
Rapid screening mitochondrial DNA mutation by using denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography
Abstract
Aim: To optimize conditions of DHPLC and analyze the effectiveness of various DNA polymerases on DHPLC resolution, and evaluate the sensitivity of DHPLC in the mutation screening of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA).
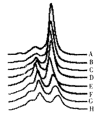
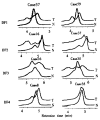
Methods: Two fragments of 16s gene of mitochondrial DNA (one of them F2 is a mutant fragment) and an A3243G mutated fragment were used to analyze the UV detection limit and determine the minimum percentage of mutant PCR products for DHPLC and evaluate effects of DNA polymerases on resolution of DHPLC. Under the optimal conditions, we analyzed the mtDNA mutations from muscle tissues of mitochondrial encephalomyopathy with lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) and screened blindly for variances in D-loop region of mtDNA from human gastric tumor specimen.
Results: Ten A3243G variants were detected in 12 cases of MELAS, no alterations were detected in controls and these results were consistent with the results obtained by analysis of RFLP with ApaI. We also identified 26 D-loop variances in 46 cases of human gastric cancer tissues and 38 alterations in 13 gastric cancer cell lines. The mutation of mtDNA at 80 ng PCR products containing a minimum of 5% mutant sequences could be detected by using DHPLC with UV detector. Moreover, Ampli-Taq Gold polymerase was equally as good as the proofreading DNA polymerase (e.g., Pfu) in eliminating the false positive produced by Taq DNA polymerases.
Conclusion: DHPLC is a powerful, rapid and sensitive mutation screening method for mtDNA. Proofreading DNA polymerase is more suitable for DHPLC analysis than Taq polymerase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Influence of DNA polymerases on mutation screening of denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography].Ai Zheng. 2002 Oct;21(10):1160-3. Ai Zheng. 2002. PMID: 12508666 Chinese.
-
Rapid screening of the entire mitochondrial DNA for low-level heteroplasmic mutations.Mitochondrion. 2005 Aug;5(4):282-96. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2005.06.001. Mitochondrion. 2005. PMID: 16050991
-
Mutation screening of the mitochondrial genome using denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography.Mol Genet Metab. 2005 Jan;84(1):61-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2004.09.011. Epub 2004 Nov 11. Mol Genet Metab. 2005. PMID: 15639196
-
Mitochondrial diseases.Curr Opin Neurol Neurosurg. 1992 Oct;5(5):622-32. Curr Opin Neurol Neurosurg. 1992. PMID: 1392136 Review.
-
DNA mutation detection using denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC).Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2006 Feb;Chapter 7:Unit7.10. doi: 10.1002/0471142905.hg0710s48. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2006. PMID: 18428395 Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA microsatellite instability in hepatocellular carcinoma in Chinese.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Feb 1;10(3):371-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i3.371. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 14760760 Free PMC article.
-
Somatic mutation analysis of p53 and ST7 tumor suppressor genes in gastric carcinoma by DHPLC.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Dec;9(12):2662-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2662. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 14669308 Free PMC article.
-
Association between pepsinogen C gene polymorphism and genetic predisposition to gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Jan;9(1):50-3. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i1.50. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12508350 Free PMC article.
-
An oligonucleotide microarray for high-throughput sequencing of the mitochondrial genome.J Mol Diagn. 2006 Sep;8(4):476-82. doi: 10.2353/jmoldx.2006.060008. J Mol Diagn. 2006. PMID: 16931588 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial microsatellite instability in gastric cancer and its precancerous lesions.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Mar 15;10(6):800-3. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i6.800. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15040020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao X, Cai YY, Xie DW, Wang LD, Yang CS. Multiplex PCR SSCP: a highly effective and efficient method of mutation detection and analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 1998;4:106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

