The promoting molecular mechanism of alpha-fetoprotein on the growth of human hepatoma Bel7402 cell line
- PMID: 12046072
- PMCID: PMC4656423
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i3.469
The promoting molecular mechanism of alpha-fetoprotein on the growth of human hepatoma Bel7402 cell line
Abstract
Aim: The goal of this study was to characterize the AFP receptor, its possible signal transduction pathway and its proliferative functions in human hepatoma cell line Bel 7402.
Methods: Cell proliferation enhanced by AFP was detected by MTT assay, 3H-thymidine incorporation and S-stage percentage of cell cycle analysis. With radioactive labeled 125I-AFP for receptor binding assay; cAMP accumulation, protein kinase A activity were detected by radioactive immunosorbent assay and the change of intracellular free calcium (Ca2+i) was monitored by scanning fluorescence intensity under TCS-NT confocal microscope. The expression of oncogenes N- ras, p 53, and p21( ras ) in the cultured cells in vitro were detected by Northern blotting and Western blotting respectively.
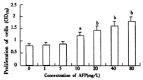
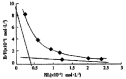
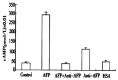
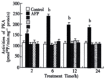
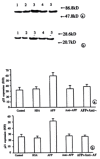
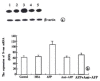
Results: It was demonstrated that AFP enhanced the proliferation of human hepatoma Bel 7402 cell in a dose dependent fashion as shown in MTT assay, (3)H-thymidine incorporation and S-phase percentage up to 2-fold. Two subtypes of AFP receptors were identified in the cells with Kds of 1.3 x 10(-9)mol.L(-1) and 9.9 x10(-8)mol. (-1)L respectively. Pretreatment of cells with AFP resulted in a significant increase (625%) in cAMP accumulation. The activity of protein kinase A activity were increased up to 37.5, 122.6, 73.7 and 61.2% at treatment time point 2, 6, 12 and 24 hours. The level of intracellular calcium were elevated after the treatment of alpha-fetoprotein and achieved to 204% at 4 min. The results also showed that AFP(20mg.L(-1)) could upregulate the expression of N- ras oncogenes and p 53 and p21( ras ) in Bel 7402 cells. In the later case,the alteration were 81.1%(12h) and 97.3%(12h) respectively compared with control.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate that AFP is a potential growth factor to promote the proliferation of human hepatoma Bel 7402 cells. Its growth-regulatory effects are mediated by its specific plasma membrane receptors coupled with its transmembrane signaling transduction through the pathway of cAMP-PKA and intracellular calcium to regulate the expression of oncogenes.
Figures


References
-
- Mizejewski GJ, Warner AS. Alpha-fetoprotein can regulate growth in the uterus of the immature and adult ovariectomized mouse. J Reprod Fertil. 1989;85:177–185. - PubMed
-
- Keel BA, Eddy KB, Cho S, May JV. Synergistic action of purified alpha-fetoprotein and growth factors on the proliferation of porcine granulosa cells in monolayer culture. Endocrinology. 1991;129:217–225. - PubMed
-
- Wang W, Alpert E. Downregulation of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta production and gene expression in human monocytic cells by human alpha-fetoprotein. Hepatology. 1995;22:921–928. - PubMed
-
- Mizejewski GJ. alpha-fetoprotein as a biologic response modifier: relevance to domain and subdomain structure. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1997;215:333–362. - PubMed
-
- Dudich E, Semenkova L, Gorbatova E, Dudich I, Khromykh L, Tatulov E, Grechko G, Sukhikh G. Growth-regulative activity of human alpha-fetoprotein for different types of tumor and normal cells. Tumour Biol. 1998;19:30–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

