Host responses to Renibacterium salmoninarum and specific components of the pathogen reveal the mechanisms of immune suppression and activation
- PMID: 12047757
- PMCID: PMC1782716
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2002.01420.x
Host responses to Renibacterium salmoninarum and specific components of the pathogen reveal the mechanisms of immune suppression and activation
Abstract
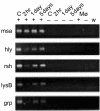
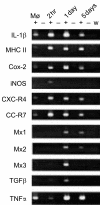
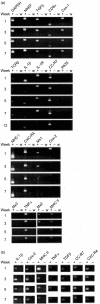
During infection, Renibacterium salmoninarum survives within the pronephric macrophages of salmonid fish. Therefore, to study the initial phases of the interaction we infected macrophages with live bacteria and analysed the responses of host and pathogen. It was found that the expression of msa encoding the p57 antigen of R. salmoninarum, was constitutive, while the expression of hly and rsh, encoding haemolysins, and lysB and grp was reduced after infection. Macrophages showed a rapid inflammatory response in which the expression of interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC II), inducible cyclo-oxygenase (Cox-2), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) was enhanced, but tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) expression was greatly reduced initially and then increased. After 5 days, except for TNF-alpha and MHC II, expression returned to levels approaching those of uninfected macrophages. We propose that R. salmoninarum survives initial contact with macrophages by avoiding and/or interfering with TNF-alpha-dependent killing pathways. The effects of specific R. salmoninarum components were studied in vivo by injecting fish with DNA vaccine constructs expressing msa, hly, rsh, lysB, or grp. We found that msa reduced the expression of IL-1beta, Cox-2, and MHC II but stimulated TNF-alpha while hly, rsh and grp stimulated MHC II but down-regulated TNF-alpha. Constructs expressing hly or lysB stimulated iNOS expression and additionally, lysB stimulated TNF-alpha. The results show how p57 suppresses the host immune system and suggest that the immune mechanisms for the containment of R. salmoninarum infections rely on MHC II- and TNF-alpha-dependent pathways. Moreover, prolonged stimulation of TNF-alpha may contribute to the chronic inflammatory pathology of bacterial kidney disease.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of a whole cell, p57- vaccine against Renibacterium salmoninarum.Dis Aquat Organ. 1999 Apr 15;36(1):37-44. doi: 10.3354/dao036037. Dis Aquat Organ. 1999. PMID: 10349551
-
Production of the 57 kDa major surface antigen by a non-agglutinating strain of the fish pathogen Renibacterium salmoninarum.Dis Aquat Organ. 1999 Oct 11;38(1):23-31. doi: 10.3354/dao038023. Dis Aquat Organ. 1999. PMID: 10590925
-
Differential expression of the virulence-associated protein p57 and characterization of its duplicated gene msa in virulent and attenuated strains of Renibacterium salmoninarum.Dis Aquat Organ. 1999 Nov 8;38(2):115-23. doi: 10.3354/dao038115. Dis Aquat Organ. 1999. PMID: 10598282
-
Immunization with bacterial antigens: bacterial kidney disease.Dev Biol Stand. 1997;90:145-52. Dev Biol Stand. 1997. PMID: 9270843 Review.
-
Genomic and proteomic aspects of p57 protein from Renibacterium salmoninarum: Characteristics in virulence patterns.Microb Pathog. 2023 Jan;174:105932. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105932. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Microb Pathog. 2023. PMID: 36473669 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of co-infections on fish: a review.Vet Res. 2016 Oct 4;47(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s13567-016-0383-4. Vet Res. 2016. PMID: 27716438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atlantic Salmon Pre-smolt Survivors of Renibacterium salmoninarum Infection Show Inhibited Cell-Mediated Adaptive Immune Response and a Higher Risk of Death During the Late Stage of Infection at Lower Water Temperatures.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 30;11:1378. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01378. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32695119 Free PMC article.
-
Host-Pathogen Interactions of Marine Gram-Positive Bacteria.Biology (Basel). 2022 Sep 5;11(9):1316. doi: 10.3390/biology11091316. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36138795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential immune gene response in gills, skin, and spleen of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss infected by Ichthyophthirius multifiliis.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 20;14(6):e0218630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218630. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31220151 Free PMC article.
-
The Immune Response to the Myxozoan Parasite Myxobolus cerebralis in Salmonids: A Review on Whirling Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 12;24(24):17392. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417392. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139218 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Evelyn TPT. Bacterial kidney disease-BKD. In: Inglis V, Roberts RJ, Bromage NR, editors. Bacterial Diseases of Fish. Oxford: Blackwell; 1993. pp. 177–95.
-
- Gutenberger SK, Duimstra JR, Rohovec JS, Fryer JL. Intracellular survival of Renibacterium salmoninarum in trout mononuclear phagocytes. Dis Aquat Org. 1997;28:93–106.
-
- Evelyn TPT, Prosperi-Porta L, Ketcheson JE. Further evidence for the presence of Renibacterium salmoninarum in salmonid eggs and for the failure of povidone-iodine to reduce the intra-ovum infection in water-hardened eggs. J Fish Dis. 1984;7:173–82.
-
- Balfry SK, Albright LJ, Evelyn TPT. Horizontal transfer of Renibacterium salmoninarum among farmed salmonids via the fecal-oral route. Dis Aquat Org. 1996;25:63–9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

